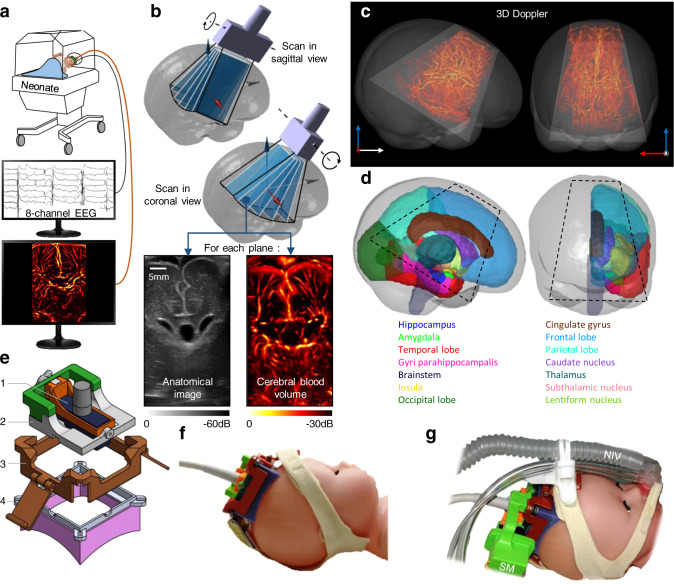
Fig. 1. fUS recording and brain atlas registration.
a Simultaneous acquisition of an eight-electrodes EEG and fUS on neonates kept in their incubators. b 3D ultrasound tomography combining motorized plane-by-plane scans in coronal and sagittal views. The anatomic B-Mode image and the vascular doppler image are acquired in each plane. Only one scan in each orientation was needed for each patient. c In dark gray, sagittal and coronal view of a MRI T1 volume of a 28 weeks PMA preterm neonate. Trapezoid in light gray: brain volume accessible with fUS. In red, the 3D vasculature from Doppler tomography is overlaid. d Brain areas in the right hemisphere of a 28 weeks PMA preterm neonate, segmented according to Makropoulos atlas. Dashed black lines demarcate the ultrasound-accessible structures. e Detail of the 3D-printed headset. (1) Ultrasound probe. (2) Probe-holder with rotation axis. (3) Straps holder. (4) Cap with magnets to secure the probe-holder, and silicon casting adapted to the patient skull. f Ultrasound probe inserted in the headset, and secured to the model head using headgear’s straps. g Motorized version of the probe-holder with as servomotor (SM), compatible with the non-invasive ventilation system (NIV) commonly used on very preterm patient.