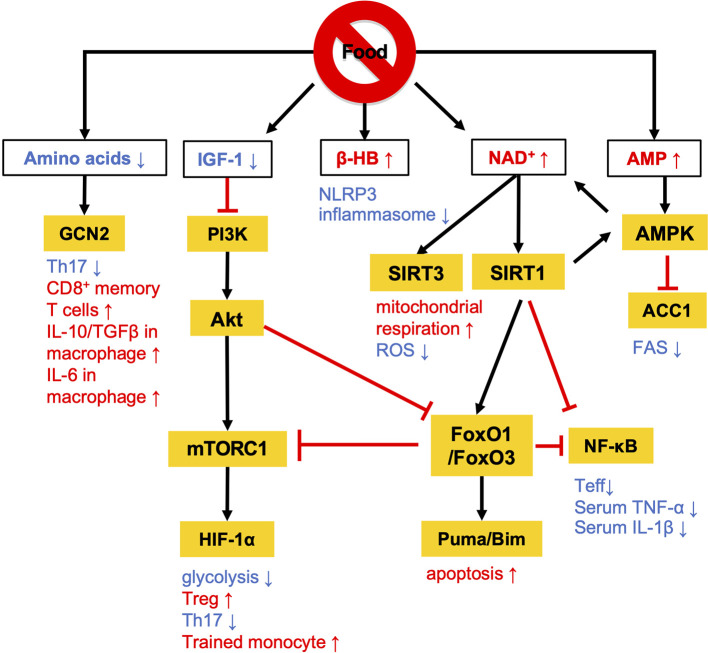
Figure 1.
Overview of the nutritional signals regulating immune responses. Calorie restriction (CR) and fasting lowers plasma IGF-1 levels and downregulates PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. At a low-energy status, two major energy sensors: adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and sirtuin 1 (SIRT) family proteins, are activated by AMP and NAD+, respectively. GCN2 acts as a sensor of amino acid deficiency to regulate the differentiation and polarization of T cells and macrophages. β-HB also contributes to the anti-inflammatory effects by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation. The white and orange boxes represent signal messengers and enzymes/transcription factors, respectively. The pathways depicted by black arrows and red bars represent the activation and inhibition by dietary restriction, respectively.