Figure 2.
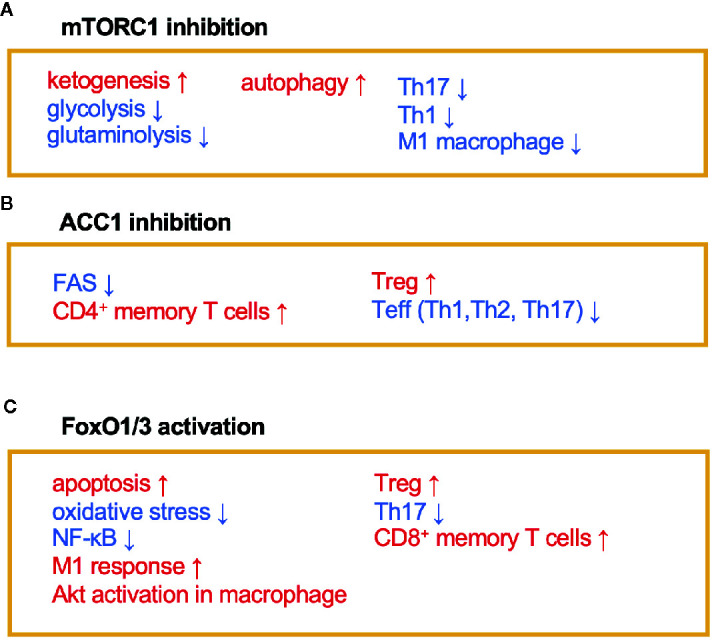
The immunomodulating effects of mTORC1, ACC1, and FoxO1/3. Fasting or calorie restriction (CR) suppresses mTORC1 and ACC1 activation and activates FoxO1/3 pathways. (A) mTORC1 inhibition enhances ketogenesis and reduces glycolysis and glutaminolysis. mTORC1 inhibition also induces autophagy in macrophage and suppresses Th1, Th17, and M1 macrophage differentiation. (B) ACC1 inhibition reduces FAS, which facilitates development of CD4+ memory T cells and Treg cells and conversely suppresses Teff (Th1, Th2, and Th17) responses. (C) Activation of FoxO1 and/or FoxO3 induces apoptosis and inactivates NF-κB. FoxO1 or FoxO3 also regulates phenotypes of macrophages, suppresses Th17 response, and induces development of CD8+ memory T cells and Treg cells.
