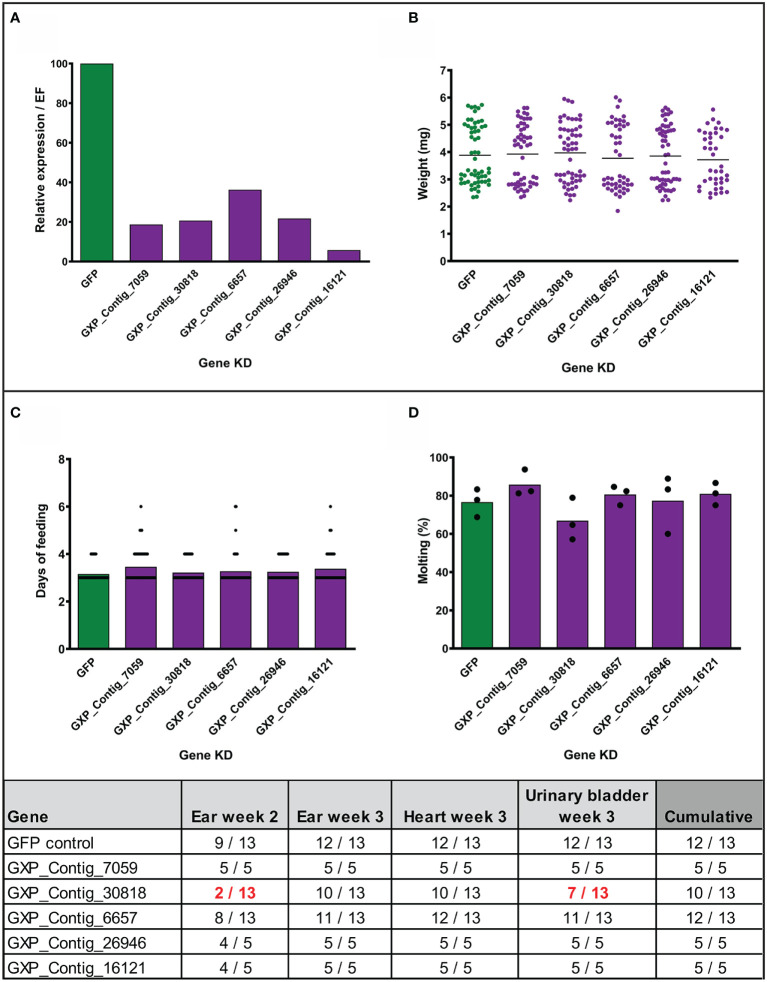
Figure 4.
Effect of gene silencing by RNA interference on nymph feeding and Borrelia afzelii transmission. (Upper) Silencing of five tick genes in uninfected nymphs. (A) Evaluation of the silencing level by qRT-PCR (each group represents a mix of five fully fed nymphs). (B) Weights of individual fully fed nymphs. Each dot represents a single tick. (C) Duration of nymph feeding. (D) Molting success of fully fed nymphs into adults (percentage of molted nymphs fed on each mouse; biological triplicates). (Lower) Summary table of two transmission experiments with the gene-silenced B. afzelii-infected nymphs. Numbers indicate total qRT-PCR positive/total mouse tissues during the infection (ear week 2) and after mice scarification (week 3). dsGFP was used as a negative control. A decrease of positivity by >25% is highlighted in red.