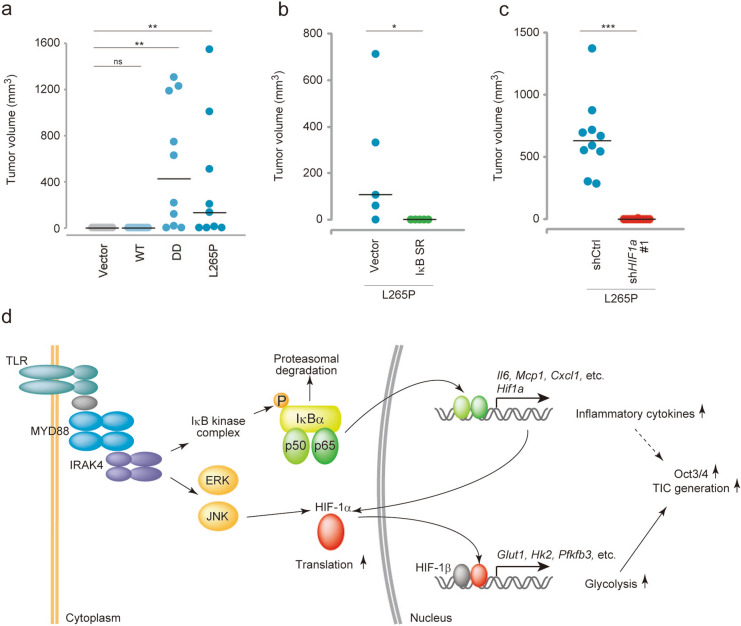
Figure 8.
MYD88 L265P expressing p53−/−MEFs form tumours via the NF-κB-HIF-1α axis. (a–c) Tumourigenesis experiments in vivo. Tumour sizes were monitored weekly. (a) The indicated gene-expressing p53−/−MEFs (2.5 × 106 cells) were subcutaneously injected into 7-week-old nude mice (n = 10 per group, except L265P, n = 9). One mouse in the L265P group formed a tumour and was eliminated from this statistical analysis because of unknown death. (b) Vector or IκBSR introduced MYD88 L265P-expressing p53−/−MEFs (1.6 × 106 cells) were subcutaneously injected into 7-week-old nude mice (n = 6 per group). (c) shCtrl or shHif1a introduced MYD88 L265P-expressing p53−/−MEFs (2.5 × 106 cells) were subcutaneously injected into 7-week-old nude mice (n = 10 per group). (d) A graphical depiction of the mechanism of MYD88-induced TIC generation from p53−/−MEFs. (a–c) For the statistical analysis, the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by the Steel–Dwass test as a post-hoc test were used for (a) and the Mann–Whitney U-test was used for (b,c) *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.