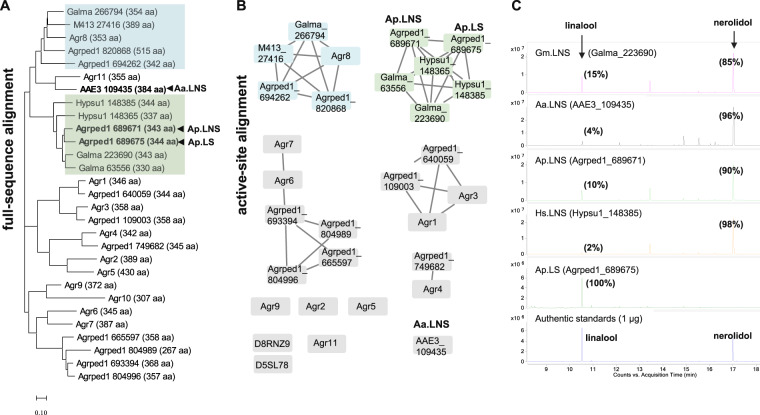
Fig. 3. Sequence analysis of fungal TPS homologs.
A Phylogenetic tree based on full-sequence alignment consisting of 12 TPS homologs from A. aegerita (Aa.LNS and Agr), 11 from A. pediades (Ap.LS, Ap.LNS and Agrped1), 3 from Galerina marginata (Galma), 2 from Hypholoma sublateritium (Hypsu1), and 1 from Hebeloma cylindrosporum (M413_27416). B Sequence similarity network (SSN) built on the predicted active sites (Supplementary Table S1). Agr10 is excluded as it shares limited similarity to the templates (PDB ID: 4LXM and 5NX5). Instead, D5SL78 from Streptomyces clavuligerus and D8RNZ9 from Selaginella moellendorffii (Spikemoss) are included. The rest of the candidates are the same as those of full-sequence alignment. LNS and muurolene/cadinene synthase groups are highlighted in green and blue, respectively. C Experimental validation of the predicted fungal TPS homologs. Ap.LS produced exclusively linalool; the other four produced both nerolidol (85–98%) and linalool (15–2%). Here percentage (%) refers to the peak area ratios of linalool or nerolidol to the sum of the peak areas of both substances present in each chromatogram.