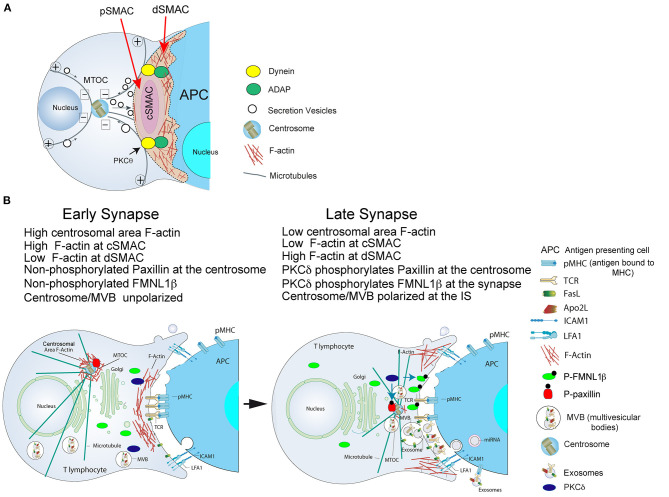
Figure 1.
(A) Cortical actin cytoskeleton reorganization and MTOC polarization. After the initial scanning contact of TCR with pMHC on the APC, both naive and effector T lymphocytes form mature IS with antigen-presenting cells (APC). Th IS lasts many hours during which de novo cytokine (i.e., IL-2, IFN-γ) production and secretion occur, that require continuous TCR signaling. Primed effector CTL establish more transient, mature IS after scanning the target cells (i.e., a virus-infected cell), and secrete lytic granules within a few minutes. Secretory vesicles (lytic granules in CTL and cytokine-containing vesicles in Th cells) are rapidly transported (several minutes for Th cells and very few minutes or seconds for effector CTL) toward the MTOC (in the minus “–” direction) and, almost simultaneously, the MTOC polarizes toward the cSMAC of the IS, a F-actin poor area that constitutes a secretory domain. MTOC translocation to the IS appears to be dependent on PKCθ-controlled dynein anchored to ADAP at the pSMAC, that pulls MTOC in the minus direction. In both types of IS, the initial F-actin reorganization in the cell-to-cell contact area, followed by a decrease in F-actin at the cSMAC and an accumulation of F-actin at the dSMAC appears to be involved in vesicle secretion. (B) Actin cytoskeleton reorganization events occurring at the CD4+ Jurkat T lymphocyte IS model: PKCδ and MTOC/MVB polarization: both FMNL1β and paxillin are phosphorylated by PKCδ. Before forming the IS, both FMNL1β (in the cytosol) and paxillin (located at the centrosome), proteins that regulate the assembly and disassembly of F-actin, are dephosphorylated, which keeps them inactive. Left: in an early IS there is an accumulation of F-actin in the central region of the IS, while the centrosome is surrounded by a dense F-actin network that keeps it retained near the nucleus and away from the IS. Right: after PKCδ is activated by TCR stimulation at the IS, FMNL1β is phosphorylated in the C-terminal, DAD autoinhibitory domain, and is located in the IS (P-FMNL1β). In addition, paxillin is phosphorylated in Threonine 538 and remains located in the centrosome (P-paxillin). These events lead to F-actin reduction at the central region of the IS that corresponds to cSMAC, F-actin accumulation into the dSMAC and the depolymerization of F-actin surrounding the centrosome. All these processes, most probably acting in a coordinated manner, may facilitate the movement of the centrosome toward the IS and the convergence of MVB toward the F-actin depleted area in the cSMAC, which facilitates MVB fusion at the cSMAC and the subsequent secretion of exosomes (Calvo and Izquierdo, 2020) in the synaptic cleft toward the APC. For more details please refer to Herranz et al. (2019) and Bello-Gamboa et al. (2020).