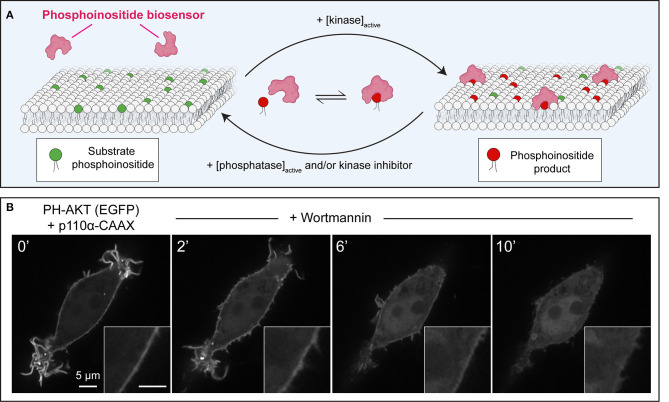
Figure 1.
Principles of operation of phosphoinositide biosensors in leukocytes. (A) Model of a generic phosphoinositide-specific biosensor in equilibrium between the cytosol and membrane following activation of the kinase that generates the target lipid, or its disappearance due to phosphatase activation, or pharmacological kinase inhibition. (B) Dynamic redistribution of the PH-AKT biosensor in response to changes in 3-phosphorylated species. PH-AKT was co-transfected with class I PI3K-CAAX into RAW264.7 cells, leading to constitutive production of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 and PtdIns(3,4)P2 at the plasma membrane. PI3Ks were then inhibited pharmacologically with wortmannin (100 nM). Note both the decrease in plasma membrane fluorescence and the concomitant increase in cytosolic GFP intensity over time.