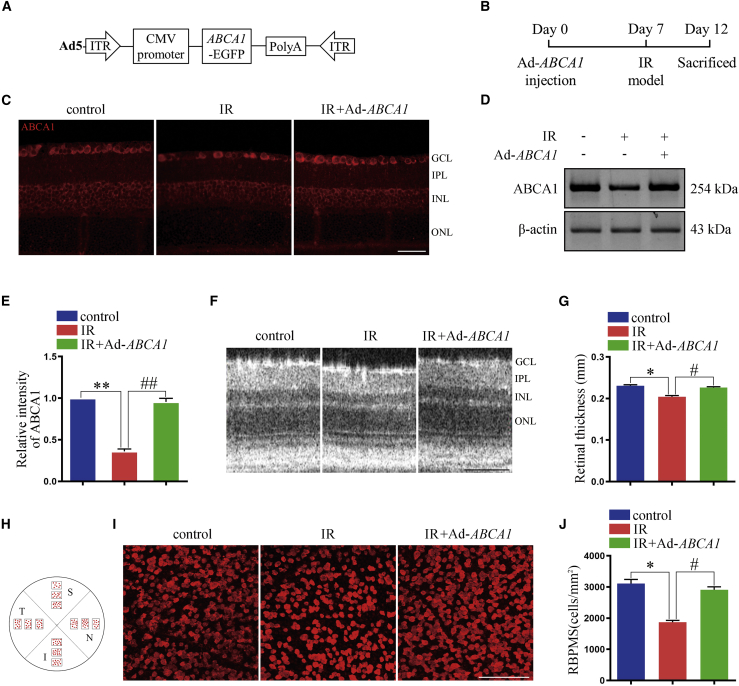
Figure 1.
The effect of Ad-ABCA1 overexpression on retina degeneration after IR in vivo
(A) Graphic illustration of the structure of Ad-ABCA1. (B) Experimental scheme of Ad-ABCA1 administration and the mouse IR model. (C) Representative immunofluorescence images for ABCA1 expression in retina slices. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Western blot analysis showing the expression of ABCA1 in retina after Ad-ABCA1 administration. These results are obtained from three independent experiments. (E) Statistical analysis of (D). ∗∗p < 0.01, compared with control retina; ##p < 0.01 compared with the IR group (n = 3 retinas per group). (F) Representative SD-OCT images for the thickness of the retina. Scale bar, 100 μm. GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; and ONL, outer nuclear layer. (G) Statistical analysis of (F). ∗p < 0.05 compared with control retina; #p < 0.05 compared with the IR group (n = 8 retinas per group). (H) Graphic illustration of the RBPMS analysis. S, superior; N, nasal; I, inferior; and T, temporal. (I) Representative immunofluorescence results showing the number of retinal ganglion cell (RGC), n = 8 retinas per group. Scale bar, 100 μm. (J) Statistical analysis of (I). ∗p < 0.05, compared with control retina; #p < 0.05 compared with the IR group. All of the data are expressed as mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey’s post hoc test.