Figure 1:
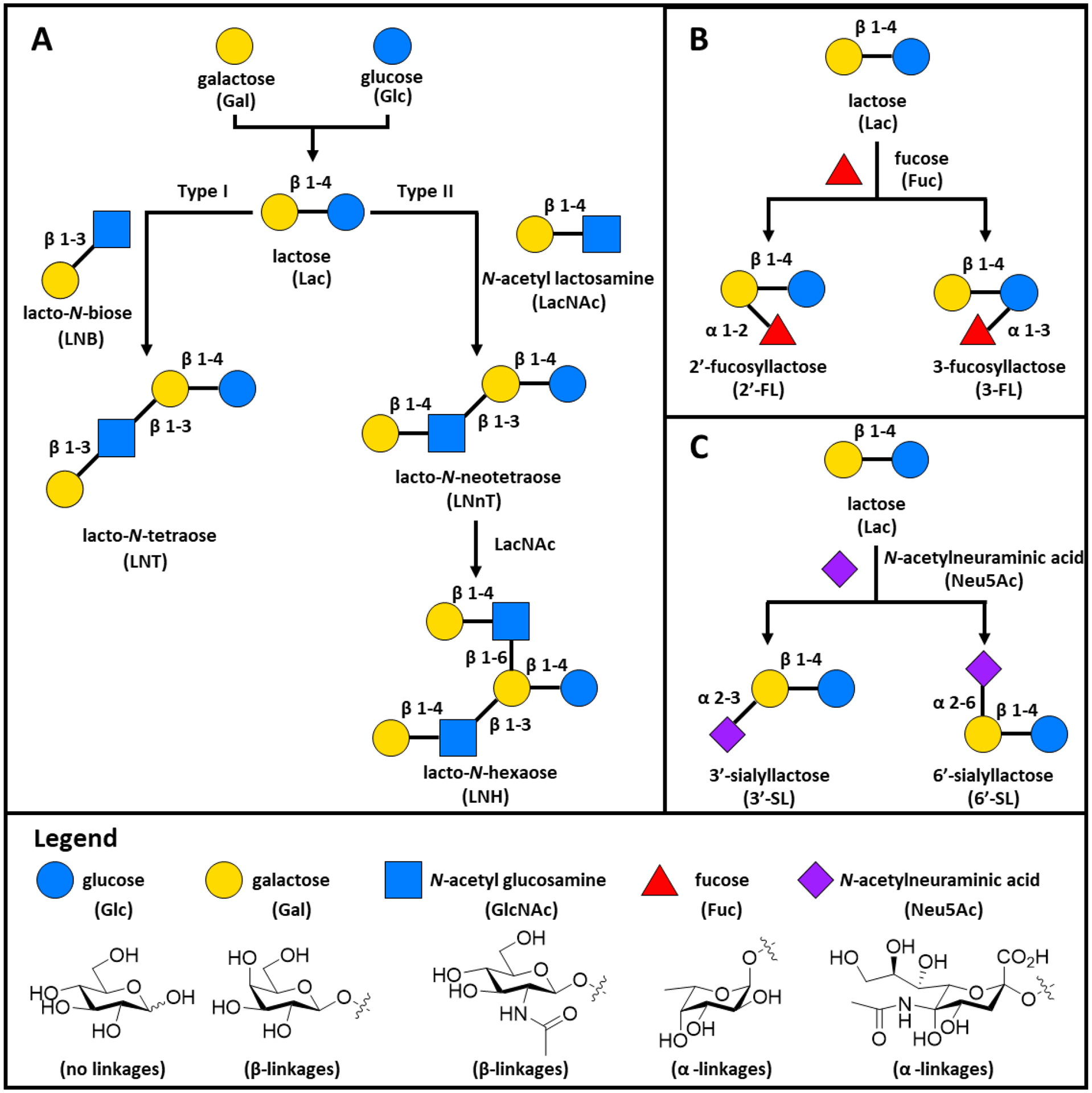
The most common human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) found in human milk and their biosynthesis. All HMOs are composed from five monosaccharides (Legend): glucose (Glc), galactose (Gal), N-acetyl glucosamine (GlcNAc), fucose (Fuc), and N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac). (A) The basic blueprint for HMO biosynthesis with lactose forming the reducing end for all oligosaccharides. Lactose (Lac) can be elongated to with either lacto-N-biose (LNB) to form type I chains, or with N-acetyl lactosamine (LacNAc) to form type II chains. B) Representative fucosylated HMOs synthesized through the addition of fucose. C) Representative sialylated HMOs characterized by the addition of N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac).
