Figure 3:
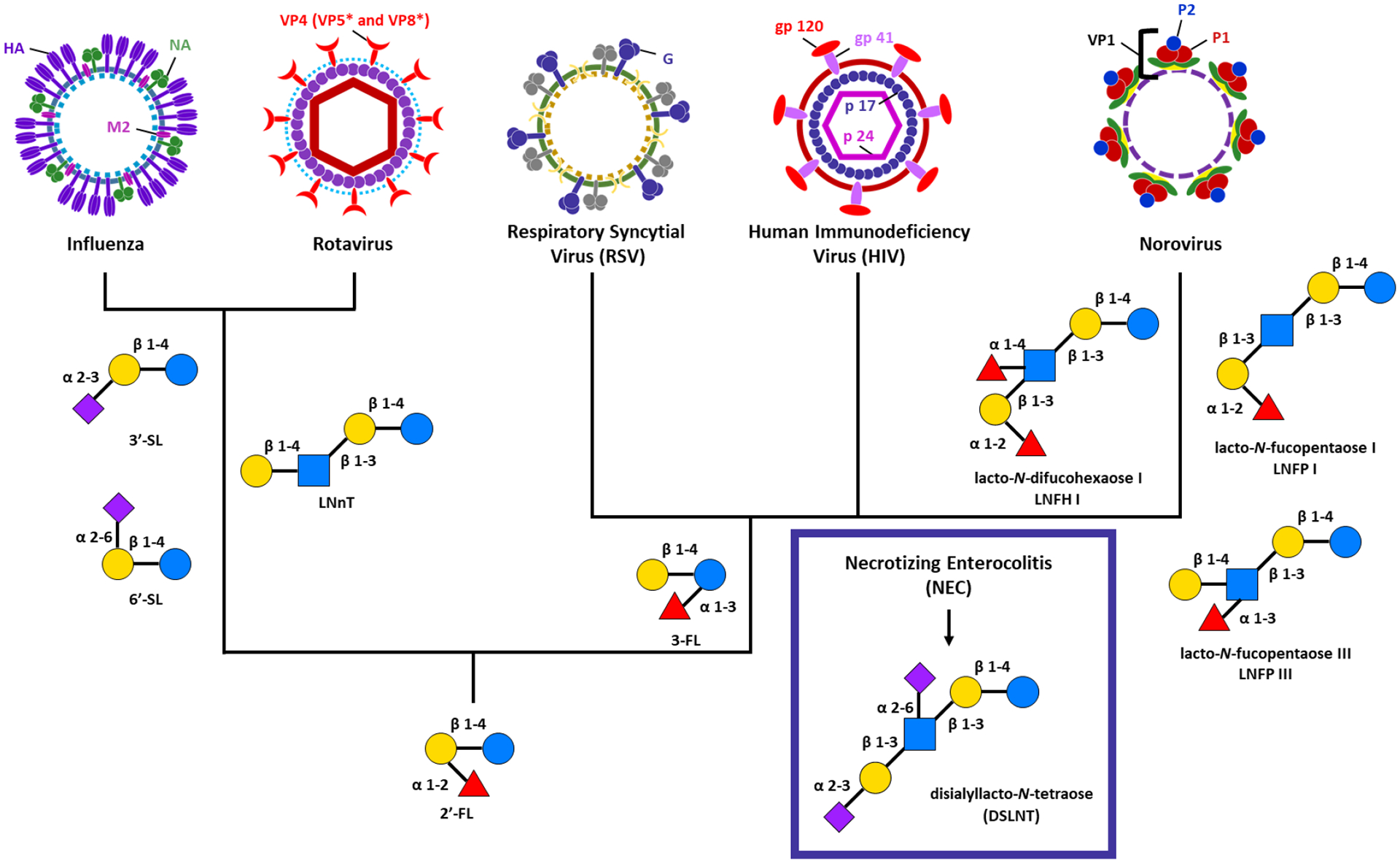
HMOs with known immunomodulatory activity against influenza, rotavirus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), norovirus and necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). With the exception of NEC, all of the viruses discussed in this review have known protection with 2’-fucosyllactose (2’-FL). Influenza and rotavirus additionally have shown reduced infection rates with 3’-sialyllactose (3’-SL), 6’-siallylactose (6’-SL), and Lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT). 3-fucosyllactose (3-FL) reduces viral load in RSV, HIV, and norovirus. lacto-N-difucohexaose LNFH I, lacto-N-fucopentaose I (LNFP I), and lacto-N-fucopentaose III (LNFP III) all also known to inhibit viral binding. Only one HMO, disialyllacto-N-tetraose (DSLNT) has been shown to reduce NEC infection.
