Fig. 3.
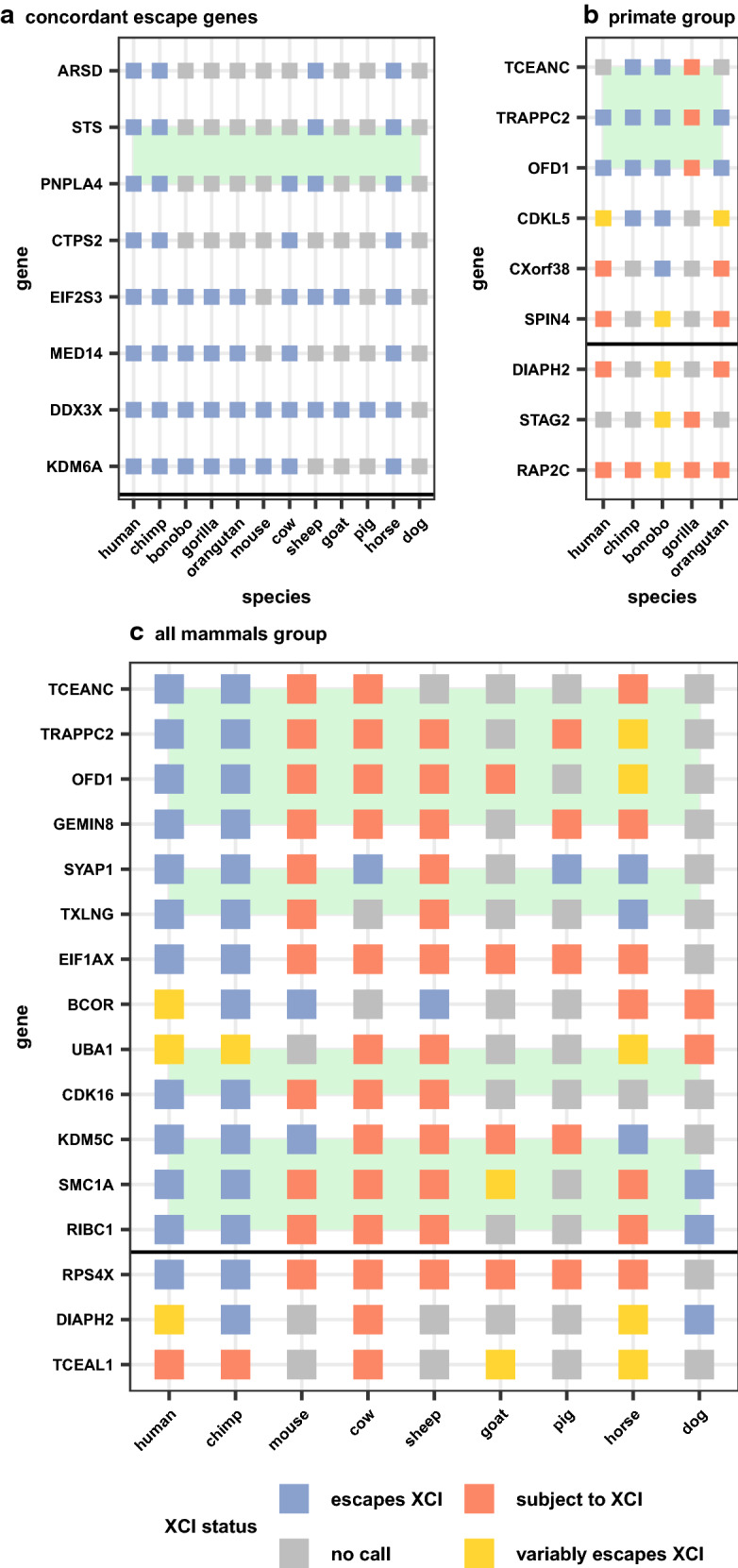
Concordant and discordant escape genes across species. Eight genes escape XCI in all informative species (a), while 259 genes were subject to XCI in all informative species (not shown). Discordant genes in two different groups of species were examined, only primates (b) and all mammals (c, limited to only 2 primate species). The intersection of a gene and species is colored based on that gene’s XCI status call in that species. Genes that did not have an XCI status call in a species are colored grey. Only escape genes informative in at least 4 + species were selected for a. Genes were selected for b if they had at least one discordant primate species while genes in c required two XCI statuses with two or more species. To match best across species within groups, 450k array data were prioritized in b and WGBS data were prioritized in c. Genes are organized based on their position on the human X chromosome with a horizontal black line denoting the centromere. Green boxes highlight domains of adjacent genes with similar changes to XCI statuses across species
