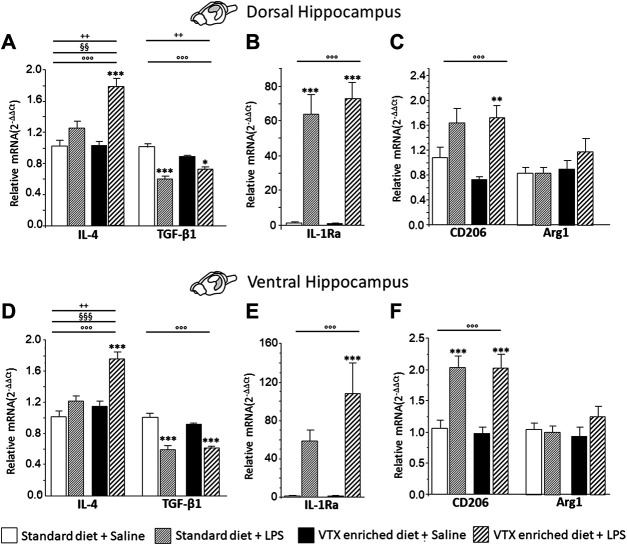
FIGURE 8.
Overall, in mice-fed VTX, an immune challenge induced a more intense anti-inflammatory response in comparison to mice-fed standard chow. Gene expression results are shown as fold changes relative to saline-treated control (standard diet) group. Bar graphs representing the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4 and TGF-β1), cytokine antagonist (IL-1Ra), or markers of microglia M2 phenotype (CD206 and Arg1) in the dorsal hippocampus (respectively, A, B, and C) or in the ventral hippocampus (respectively, D, E, and F). Treatment as indicated in the legend, n = 9–10 mice per group. Data are represented as means ± SEM and were analyzed with ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD (two-way ANOVA: ◦◦◦ p < 0.001 main effect LPS/saline; §§ p < 0.01, §§§ p < 0.001 main effect standard/VTX-enriched diet, ++ p < 0.01 LPS/saline* standard/VTX-enriched diet interaction; post hoc *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 indicate significant difference compared to saline-treated matching group).