Table 1.
The verified regulating methods and targets that could repolarize TAMs to anti-HCC phenotypes
| Phenotypic Change | Regulating method | HCC model | Pathway | Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2 to M1 | miR-99b transfection | Hepa1–6 cells injected mice |
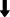 κB-Ras2 and/or mTOR; a positive feedback regulation loop of NF-κB κB-Ras2 and/or mTOR; a positive feedback regulation loop of NF-κB |
miR-99b amplifies M1 macrophage function, resulting in increased phagocytosis and antigen presentation, which impedes the growth of murine HCC [79] |
| M0 to M1; M2 to M1 | a nanoliposome-loaded C6-ceremide (LipC6) injection | C57BL/6 mice received injections of oncogenic hepatocytes |
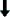 ROS signaling ROS signaling |
LipC6 enhances M1 cytokine production while inhibiting M2 cytokine production, thereby reversing immune suppression, and increasing CD8+ T cells activity [80] |
| M0 to M1; M2 to M1 | Listeria-based HCC vaccine, Lmdd-MPFG combined with PD-1 blockade | Hepa1–6/MPFG tumor-bearing mice |
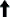 NF-κB pathway through the TLR2 and MyD88 pathway NF-κB pathway through the TLR2 and MyD88 pathway |
Lmdd-MPFG induces an increase in T cells number in the HCC TME and promotes the production of cytokines, such as IFN-γ [81]. |
| M1-type activated; M2-type decreased | dual anti-PD-1/VEGFR-2 therapy | HCA-1 in C3H mice and RIL-175 in C57Bl/6 mice. |
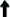 selectively upregulated pathways associated with myeloid cells and B cells selectively upregulated pathways associated with myeloid cells and B cells |
Combination PD-1and VEGFR-2 blockade therapy shifts the TAM ratios of F4/80+ CD80+ and/or CD86+ M1 TAMs to F4/80+CD206+ M2 TAMs, which also regulates the infiltration of other immune cells and reprograms the TME to an antitumor state in HCC [82]. |
| M0 to M1 | upregulate RIG-I expression | H22 liver cancer cells inoculated C57BL/6 mice |
 RIG-I/ MAVS/TRAF2/NF-κB pathway RIG-I/ MAVS/TRAF2/NF-κB pathway |
RIGI-induced M1 macrophages promoted apoptosis and death in HCC cells in vivo and in vitro [83]. |
| M0 to M1 | upregulated SIRT1 | HepG2 and RAW 264.7, HL-60 macrophages |
 NF-κB pathway NF-κB pathway |
SIRT1 overexpression enhances M1-like macrophage infiltration in HCC while inhibiting HCC cell growth, migration, and invasion [84]. |
| M2 to M1 | upregulate IL-37 expression | HepG2 and Huh-7 cells injected BALB/c nude mice and HCC-conditioned TAMs |
 IL-6/STAT3 signaling. IL-6/STAT3 signaling. |
IL-37 inhibits M2 polarization of TAMs and then suppresses HCC cell activities, including growth, migration, and invasion. In vivo, upregulated IL-37 expression in HCC-conditioned TAMs delays tumor growth [85]. |
| M2 to M1 | miR-98 mimics | HepG2 and SMMC7721 cells incubated with the culture medium of TAMs |
 targeting IL-10 targeting IL-10 |
miR-98 reverses M2 polarization in HCC and inhibits the TAM-mediated promotion of invasion, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HCC [86, 87]. |
