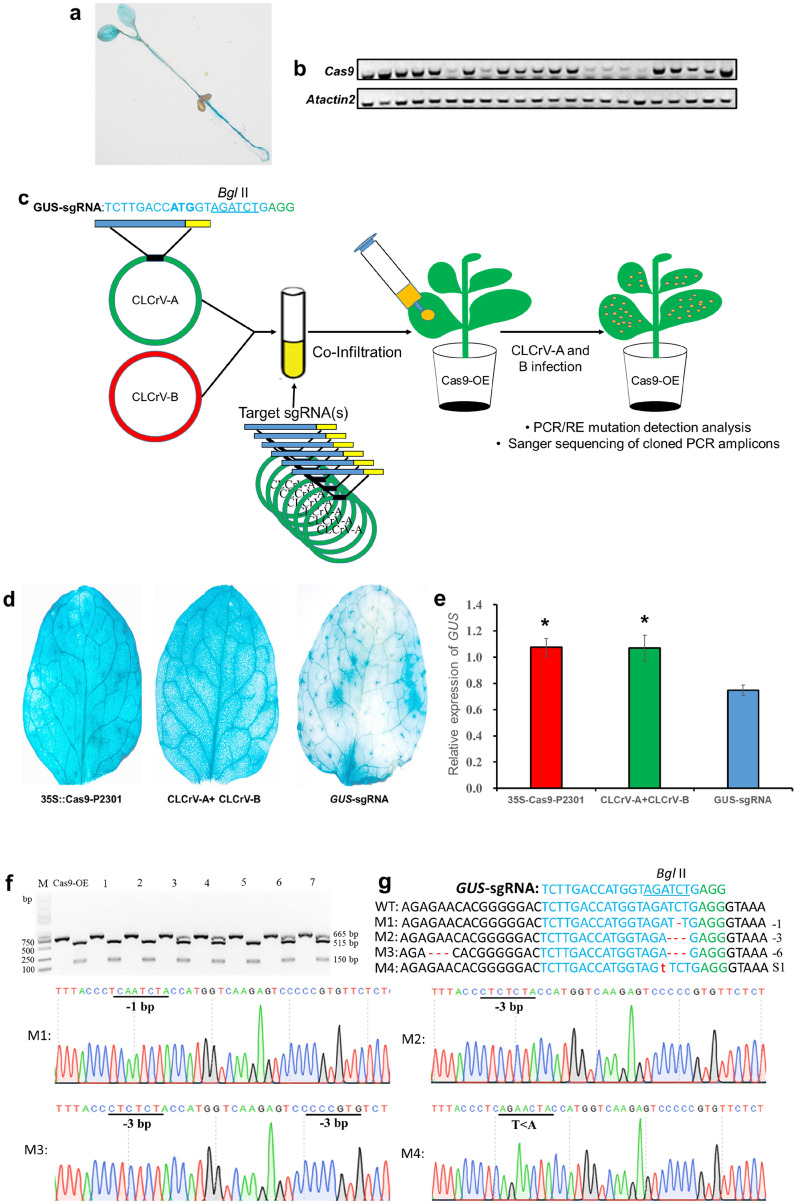
Fig. 1.
GUS reporter gene system targeted by CLCrV-mediated VIGE. a GUS staining of Cas9-OE A. thaliana seedling. b Cas9 expression levels in transgenic plants determined by RT-PCR. c Experimental scheme of the CLCrV-mediated genome editing. d GUS staining in Cas9-OE A. thaliana leaves infiltrated with Agrobacterium carrying different constructs. GUS staining of leaves inoculated with CLCrV-A and CLCrV-B empty vectors that served as a control, the blue area of leaves inoculated with GUS-sgRNA decreased. e GUS expression levels determined by qRT-PCR. Asterisks indicate significant differences (* p < 0.05). f and g Detection of GUS-sgRNA targeted mutations. f Cas9-OE plant served as a control, 1–7 were plant numbers. The gel image shows PCR products of the GUS gene, and digested PCR products with BglII. g The undigested PCR products lacking the BglII site (due to the presence of a mutation) that were subsequently purified, cloned, and analyzed by sequencing. The green color indicated the PAM sequence. The BglII restriction site on the target sequence is underlined in blue. M indicates the mutation sequence. Deletions are shown in red dashes. Substitutions are denoted with red lowercase letters