Figure 3.
Molecular mechanisms of escape and comparison of N501Y RBD/269 Fab and RBD/scFv269 complexes
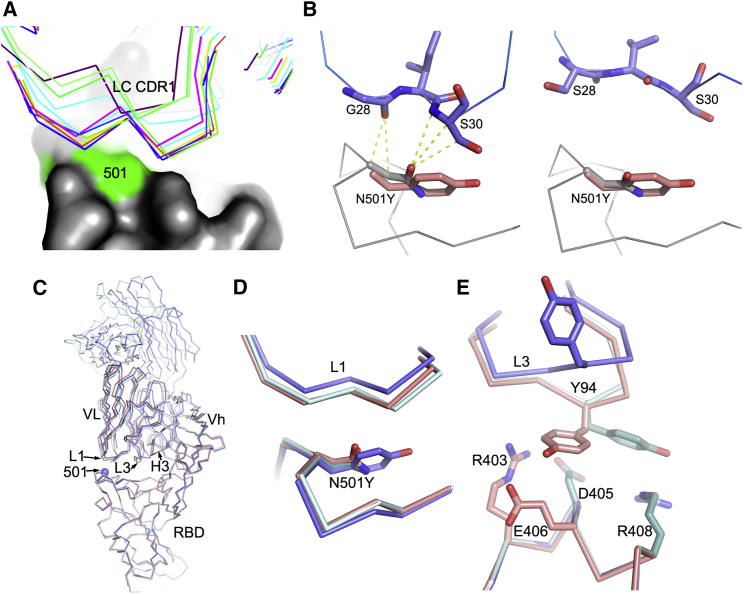
(A) CDR-L1 (thin sticks) positions of a panel of V3-53 Fabs relative to N501 on the RBD (surface, with N501 highlighted in green).
(B) The side chain of N501 makes extensive contacts with residues from CDR-L1 in the RBD-158 Fab complex (left, PDB: 7BEJ). In the right panel, N501 does not make any contact with p2c-2f11 Fab (PDB: 7CDI) whose LC is most similar in sequence and has the same CDR-L1, L2, and L3 lengths to mAb 222 shown by a blast of the LC of 222 against the PDB. The orientation and position of Y501 in the N501Y RBD/269 Fab complex is shown by overlapping the RBDs in both panels.
(C) Crystallographic structures of RBD/Fab 269, N501Y RBD/Fab 269, and RBD/scFv269. Overlay of Cαs of N501Y RBD/Fab 269 (blue) with RBD/Fab 269 (cyan) and RBD/scFv269 (salmon) by superimposing the RBDs of the three complexes (PDB: 7NEG, 7NEH, 7BEM, respectively).
(D) Structure changes in the 496–501 loop of the RBD and the CDR-L1 loop that contacts the mutation site.
(E) Structural differences of the CDR-L3 loops between the three complexes.