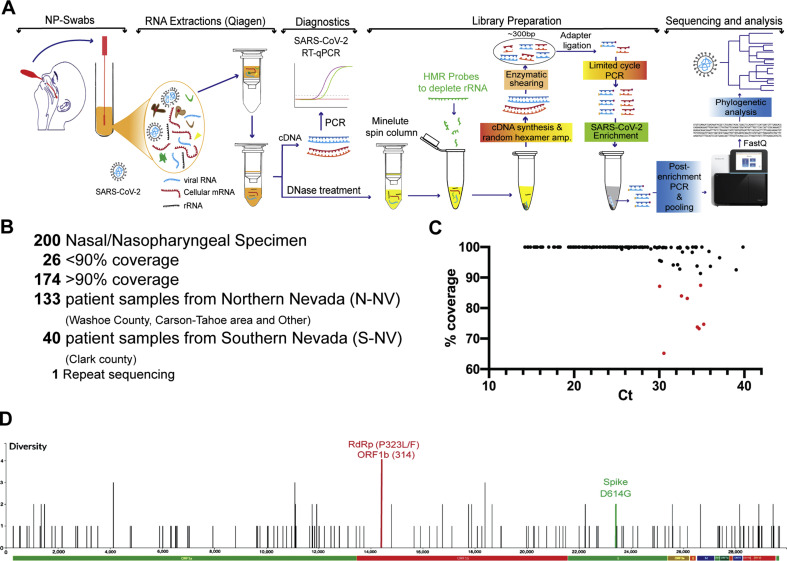
Fig. 1.
Workflow of SARS-CoV-2 genome sequencing and analysis from nasopharyngeal patient specimens in Nevada. A: RNA was extracted from nasal or nasopharyngeal (NP) swabs taken from patients in Nevada and first used to determine the presence of SARS-CoV-2 genomes by RT-qPCR. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) libraries were prepared from positive specimens; this included steps for ribosomal RNA depletion and SARS-CoV-2 enrichment. Subsequent libraries were pooled and used for whole genome sequencing at the Nevada Genomics Center on the Illumina NextSeq 500 instrument. FASTQ files were aligned to the reference genome and analyzed to determine nucleotide variation and phylogenetic relationship. B: A total of 200 specimens were sequenced, of which 173 had over 90% coverage of the SARS-CoV-2 genome. This included 133 patient specimens from Northern Nevada, 40 from Southern Nevada, and 1 specimen that was re-sequenced. C: Correlation between RT-qPCR Ct value and the percentage of coverage in the whole genome sequencing after trimming and alignment. D: Nucleotide variants across the SARS-CoV-2 genome in the 173 specimens from Nevada from March 6 to June 5.