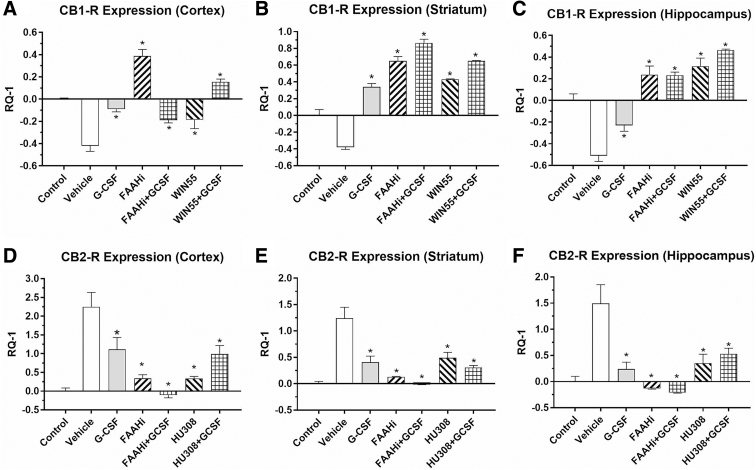
FIG. 2.
Effects of TBI on expression of CB1-R and CB2-R in brain regions (in right hemisphere, the side of injury), following 3 days of treatment with vehicle, G-CSF, FAAH inhibitor (5 mg/kg i.p.×3 days), the selective CB1 receptor agonist WIN55 (3 mg/kg i.p.×3 days), or the selective CB2 receptor agonist HU308 (3 mg/kg i.p.×3days). In the upper row (A–C), CB1-R expression was downregulated in the vehicle-treated animals compared with sham controls in the three brain regions. Treatment for 3 days after TBI with G-CSF and FAAH inhibition (and the combination of both) resulted in significant reversal of downregulation. Treatment with WIN55 (alone or in combination with G-CSF) also resulted in significant reversal of the CB1 receptor downregulation. In the lower row (D–F), CB2 receptor expression was upregulated by the injury. G-CSF alone significantly reversed the upregulation in the three brain regions. The FAAH inhibitor and HU308 (CB2 receptor agonist) each reversed the upregulation significantly, either when given alone or in combination with G-CSF (*p<0.05). One-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnett test for multiple comparisons against vehicle-treated mice (n=4 mice per treatment group).