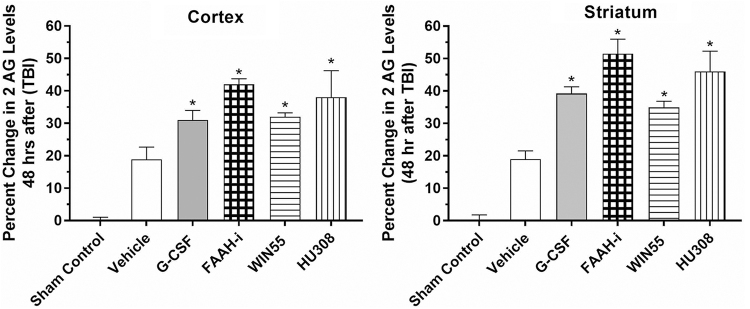
FIG. 3.
Levels of the endogenous cannabinoid ligand 2-AG in the right cerebral cortex and striatum following controlled cortical impact and treatment for 3 days with G-CSF, an inhibitor of FAAH, WIN55 (CB1 receptor agonist), and a CB2 receptor agonist (HU308). Data are expressed as percent change in 2-AG levels from vehicle treatment levels (mean vehicle control levels were 1.76±0.05 ng/g in the cortex and 1.72±0.04 ng/g in the striatum). G-CSF as well as treatment with CB1 and CB2 agonists increased levels of 2-AG in both the cortex and striatum. In addition, inhibition of the major catabolic enzyme for endocannabinoids (FAAH) also increased levels of 2-AG. One-way ANOVA, followed by the Dunnett test for multiple comparisons, showed that all treatments significantly increased 2-AG levels compared with vehicle treatments after TBI (*p<0.05). 2-AG, 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol.