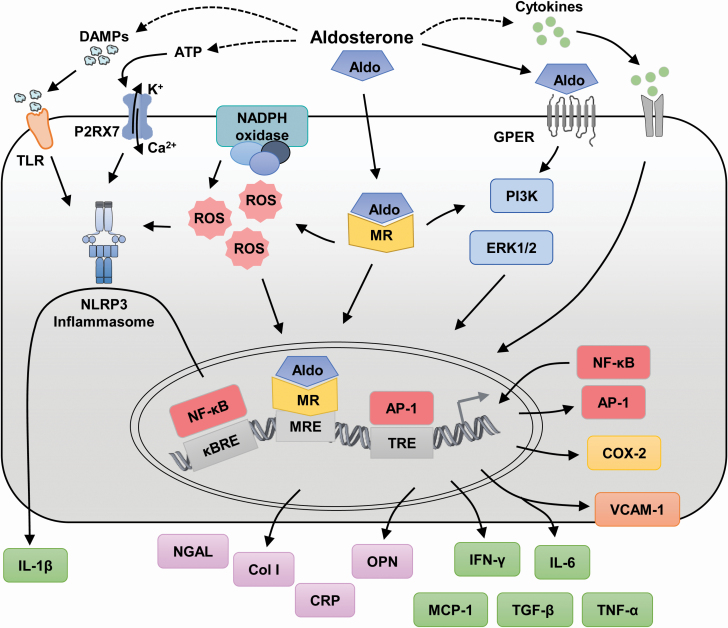
Figure 1.
Aldosterone and production of inflammatory mediators. Aldosterone induces the production of inflammatory mediators either through activation of mineralocorticoid receptors (MRs) or G-protein-coupled estrogen receptors (GPERs). The dashed line arrows indicate mechanisms not depicted in the figure. Abbreviations: Aldo, aldosterone; AP-1, activator protein-1; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; Ca2+, calcium; Col I, Collagen type I; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; CRP, C-reactive protein; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; K+, potassium; κBRE, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) response element; MCP-1, macrophage chemoattractant protein-1; MRE, MR response element; NADPH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; NGAL, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor pyrin-domain containing protein 3; OPN, osteopontin; P2RX7, P2X purinoceptor 7; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TGF, transforming growth factor; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TRE, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate response element (AP-1 response element); VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1.