FIGURE 4.
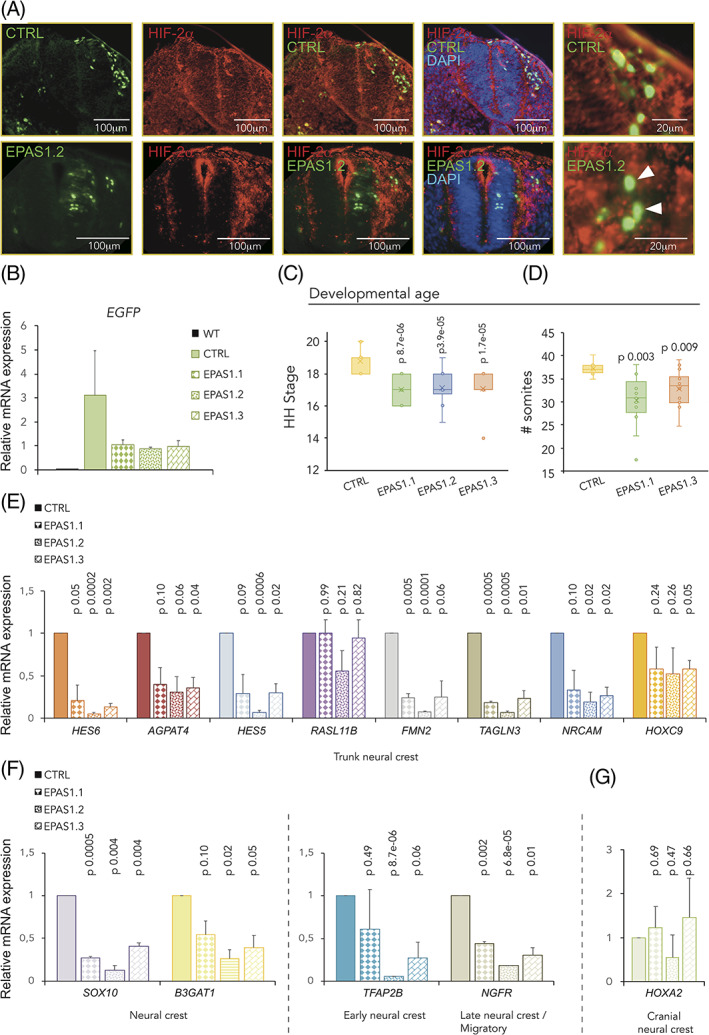
CRISPR/Cas9 mediated knockout of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)‐2α delays embryogenesis. A, Immunofluorescent staining for HIF‐2α in embryos electroporated with control (CTRL) or HIF‐2α (EPAS1.2) targeting gRNAs. Arrowheads denote GFP+ cells lacking HIF‐2α in knockout embryos. Sections from trunk. B, Relative mRNA expression measured by qRT‐PCR. WT, wild‐type HH18 embryos. C,D, Determination of developmental age 36 hours postelectroporation with a nontargeting (CTRL) gRNA compared to three different gRNAs targeting EPAS1 (EPAS1.1, EPAS1.2, EPAS1.3) as assessed by head‐ and tail morphology (converted to Hamburger Hamilton [HH] stages, C. Number of embryos analyzed were n = 14 [CTRL], n = 10 [EPAS1.1], n = 14 [EPAS1.2], and n = 14 [EPAS1.3]) or by counting somites ex ovo. (D, Number of embryos analyzed were n = 8 [CTRL], n = 13 [EPAS1.1], and n = 14 [EPAS1.3].) Statistical significance was determined by one‐way analysis of variance (ANOVA), comparing nontargeting CTRL to each individual EPAS1 gRNA. E‐G, Relative mRNA expression of trunk neural crest, E, neural crest, F, and cranial neural crest, G, associated genes in dissected trunk axial level derived neural tube tissue, measured by qRT‐PCR 36 hours postelectroporation. Data presented as mean of n = 2 biologically independent repeats, error bars denote SEM, B,E‐G. Statistical significance was determined by two‐sided student's t test, comparing nontargeting CTRL with each individual EPAS1 gRNA
