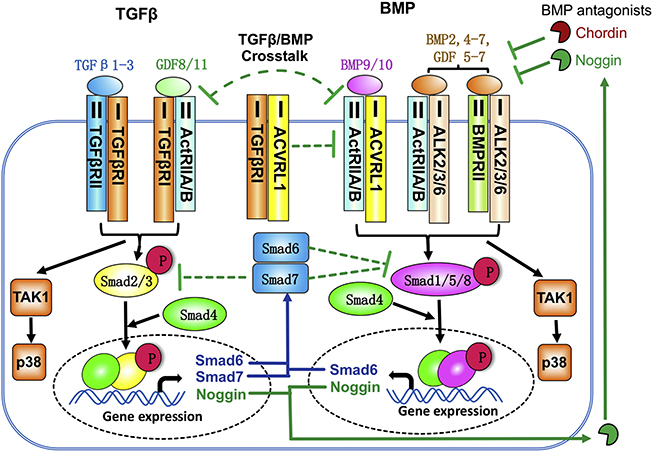
Figure. 1.
Crosstalk between TGFβ and BMP signaling. TGFB ligands bind and activate the type II TGF-B receptor and the type I receptor TGFβRI (ALK5), triggering canonical and noncanonical pathways. In the canonical pathway, transcription factors Smad2 and Smad3 are phosphorylated and associate with Smad4. This complex enters the nucleus and regulates gene expression. BMP ligands activate Smadsi, 5 and 8, which regulate a distinct set of genes. BMP ligands bind to type I BMP receptors ACVRLi (ALKi), ACVRi (ALK2), BMPRiA (ALK3), and BMPRiB (ALK6). BMPs 9/i0 are the only ligands that activate ALKi. However, the BMP type II receptors ACTRIIA and aCtRIIB can associate with either TGFβRI or with type I BMP receptors ALKi/2/3/6 to transduce either a TGFB or a BMP pathway. In addition, TGFβRI can complex with ALKi. The competition for ACTRIIA/B and binding of TGFβRI/ALKi creates a negative crosstalk between TGFβ and BMP signaling at the receptor level. Moreover, TGFβ signaling can inhitit BMP signaling by increasing Smad6, Smad7 and Noggin expression. Smad6 and Smad7 inhibit the phosphorylation and activation of Smadi/5/8. Noggin is a BMP antagonist that blocks the binding of BMPs(2,4–7) and GDFs(5–7) to receptors, but it can not antagonize BMP9 and BMP10.