Fig 4. Frequency of the top ten actionable phenotypes in Hong Kong Chinese compared to that of Africans and Europeans.
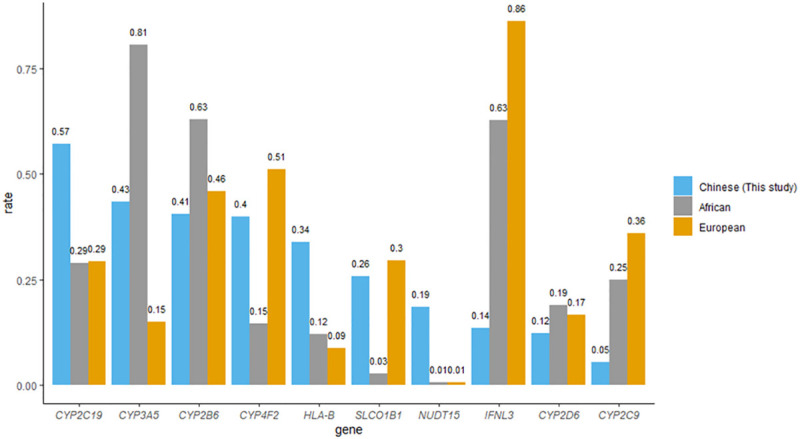
This figure compares the top ten actionable phenotypes in Hong Kong Chinese with that of Africans and Europeans. The actionable phenotype frequency of Africans and Europeans was retrieved from data from Chanfreau-Coffinier et al., Walker et al. and supplementary information in the CPIC guideline [30,36]. Actionable phenotypes include CYP2C19 IM and PM; CYP3A5 EM and IM; CYP2B6 IM and PM; carrier of CYP4F2 decreased function allele; carrier of HLA-B*15:02; *57:01 and *58:01; SLCO1B1 intermediate and low-function diplotypes; NUDT15 IM and PM; IFNL3 unfavorable response genotype; CYP2D6 UM, IM, and PM; and CYP2C9 IM and PM. CYP2C19*17 is not readily detected in exome sequencing and therefore CYP2C19 RM and UM were not included. The frequency of actionable phenotypes in CYP2C19, HLA-B, and NUDT15 was found to be higher in Hong Kong Chinese than in Europeans and Africans. In contrast, actionable genotypes in CYP3A5, CYP2B6, and CYP2D6 were more prevalent in Africans, whereas actionable phenotypes in CYP4F2, SLCO1B1, IFNL3, and CYP2C9 were more prevalent in Europeans; however, all of these genes were within the top ten actionable phenotypes in Hong Kong. IM, intermediate metabolizer; PM, poor metabolizer; EM, extensive metabolizer; UM, ultrarapid metabolizer; RM, rapid metabolizer.
