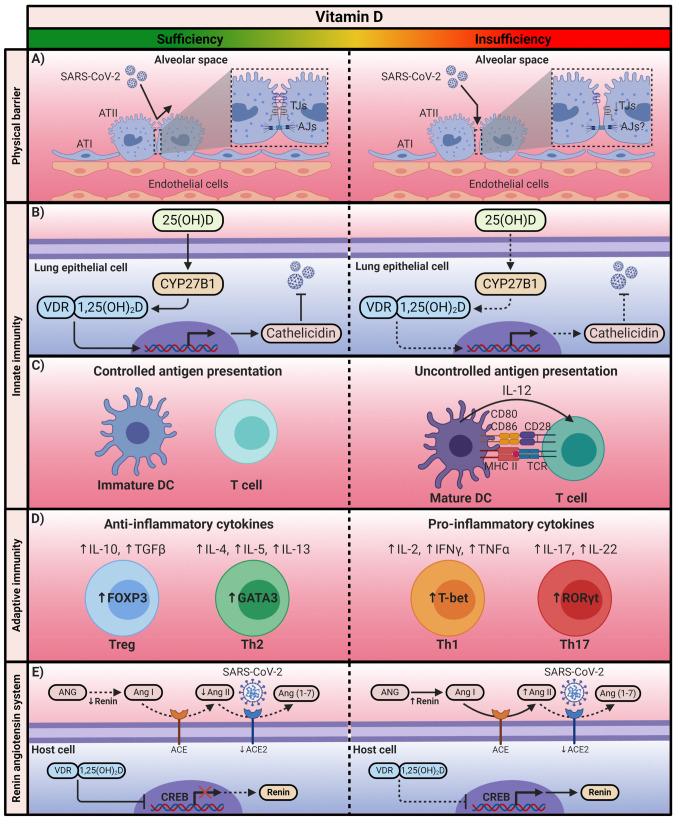
Figure 2.
The immunomodulatory mechanism of Vitamin D. Calcitriol exerts its immunomodulatory effects through the positive or negative regulation of the transcription of the genes associated with the immune system and the renin-angiotensin system. SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; 25(OH)D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D; 1,25(OH)2D, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D; VDR, vitamin D receptor; ATI, alveolar type I cell; ATII, alveolar type II cell; TJs, tight junctions; AJs, adherens junctions; CYP27B1, cytochrome P450 family 27 subfamily B member 1; DCs, dendritic cells; MCH II, major histocompatibility complex class II; TCR, T-cell receptor; FOXP3, forkhead box P3; GATA3, GATA-binding protein 3; T-bet, T-box transcription factor TBX21; RORγt, Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor γt; ANG, angiotensinogen; Ang, angiotensin; ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein. The figure was created using BioRender (https://biorender.com/).