Figure 4.
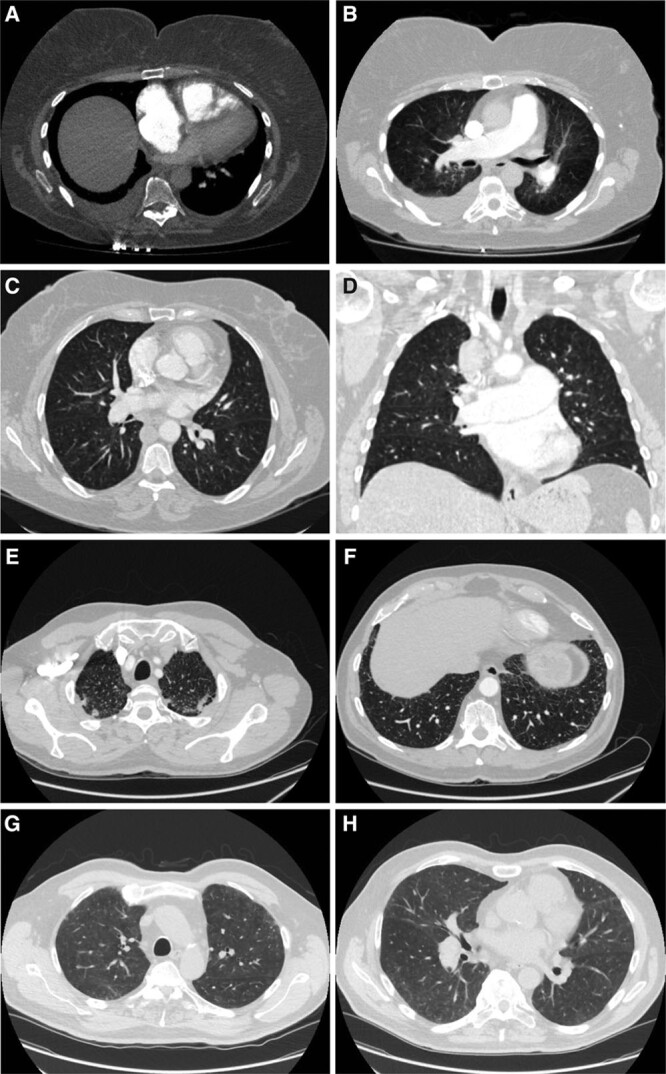
Chest computerized tomography (CT) scans of patients carrying high impact kinase insert domain receptor (KDR) mutations. A, Axial image of CT pulmonary angiogram at the level of the right ventricle (RV) moderator band, showing flattening of interventricular septum, leftwards bowing of the interatrial septum and the enlargement of the right atrium (RA) and RV, indicative of RV strain; bilateral pleural effusion, larger on the right side. B, Axial image of a pulmonary CT angiogram demonstrating enlarged pulmonary artery and mild central lung ground-glass opacity (GGO). C, Axial high-resolution CT slice of the chest in the lung window showing a trace of non-specific GGO with a central distribution. D, Coronal image showing the trace of central GGO and enlarged central pulmonary arteries. Axial high-resolution CT slice of the chest in the lung window showing apical subpleural fibrosis (E), and very minor subpleural fibrosis at the lung bases (F). Axial high-resolution CT slice of the chest in the lung window showing subpleural GGO at apical level (G), and mild GGO at mid-thoracic level (H). Patients: E001392 (A and B), E003448 (C and D), W000229 (E and F), W000274 (G and H).
