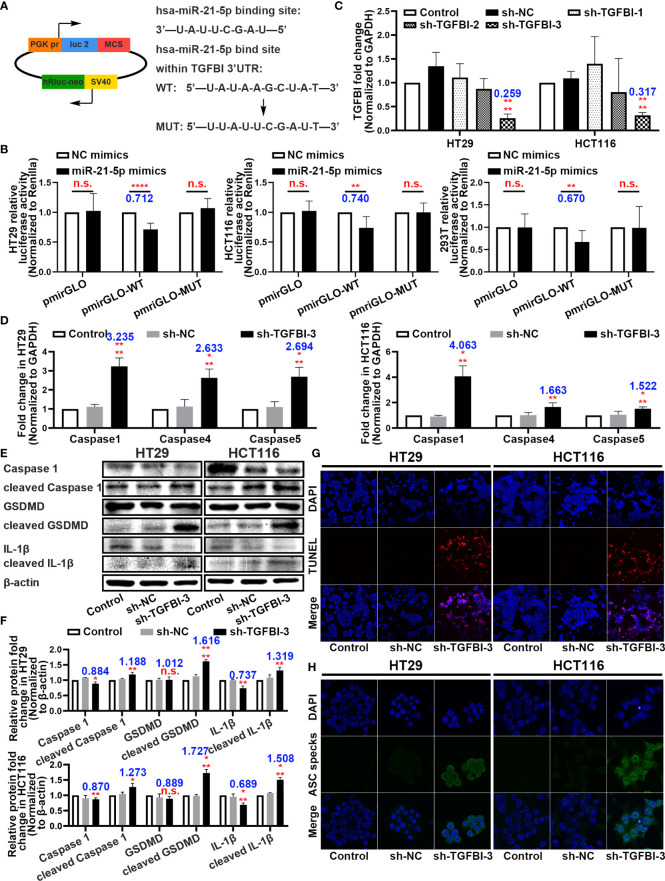
Figure 5.
Binding sites between miR-21-5p and TGFBI and function research of TGFBI in pyroptosis. (A) Predicted binding sites for miR-21-5p on TGFBI and a diagram depicting the construction of the wild-type (WT) and mutant type (MUT) pmirGLO plasmids. (B) 293T, HT29, and HCT116 cells were co-transfected with miR-21-5p/NC mimics and pmirGLO/pmirGLO-WT/pmirGLO-MUT plasmids. Luciferase activity was detected 24 h after transfection using a dual-luciferase assay. (C) Validation of TGFBI sh-RNA knockdown efficiency in HT29 and HCT116 cells as determined by qRT-PCR. (D) Pyroptosis-associated mRNA levels in HT29 and HCT116 cells after sh-TGFBI-3 transfection as determined by qRT-PCR. (E–F) Expression of Pyroptosis-associated proteins in HT29 and HCT116 cells after sh-TGFBI-3 transfection as determined by western blot analysis. (G) TUNEL stain assay of cell death in sh-TGFBI-3 transferred HT29 and HCT116 cells. (H) Immunofluorescence staining of ASC specks expression in sh-TGFBI-3 transfected HT29 and HCT116 cells.The bars and error bars indicate the mean ± SD. n.s.p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005, ****p < 0.001.