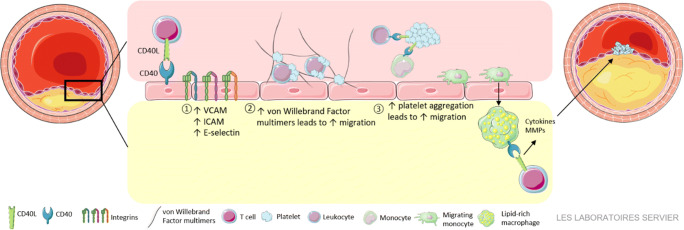
Fig. 1.
CD40-CD40L interactions in atherosclerosis. CD40-CD40L interactions stimulate leukocyte recruitment to the atherosclerotic plaque by increasing the expression of adhesion molecules on the endothelium [1], inducing the formation of ultra-large vWF multimers [2] and facilitating the formation of platelet-leukocyte aggregates [3]. In advanced atherosclerosis, CD40 activation promotes the production of MMPs, which may contribute to plaque destabilization and rupture