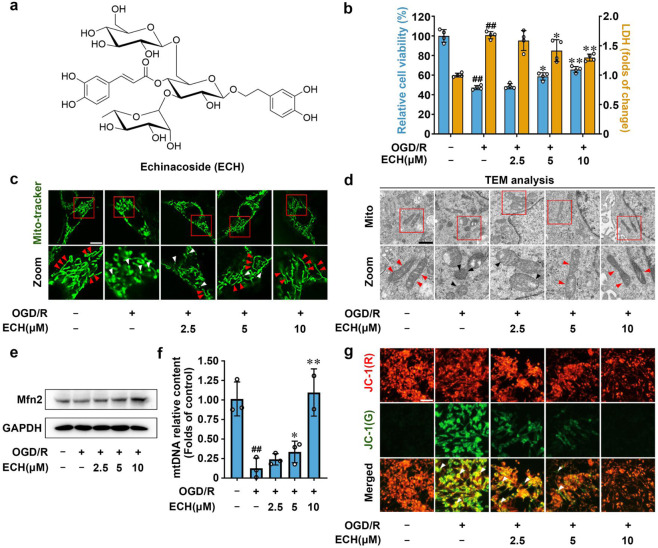
Fig. 1.
Small-molecule ECH exerts neuroprotection via promoting mitochondrial fusion. a Chemical structure of echinacoside (ECH). b ECH increased cell viability and decreased LDH release against OGD/R-induced injury in PC12 cells. c ECH promoted mitochondrial fusion against OGD/R insult in PC12 cells. Arrows (red) indicate branched healthy mitochondria. Arrows (white) indicate spherical dysfunctional mitochondria (scale bar: 20 μm). d ECH reversed the fragmented mitochondria by promoting mitochondrial fusion, which was analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Arrows (red) indicate healthy mitochondria. Arrows (black) indicate damaged mitochondria (scale bar: 0.5 μm). e ECH (10 μM) increased Mfn2 protein expression, which was analyzed by western blot. f ECH increased mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) content against OGD/R-induced injury. g ECH blocked OGD/R-induced decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), which was detected by JC-1 staining. Arrows indicate depolarized mitochondria (scale bar: 100 μm). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. ##P < 0.01 vs. control group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. OGD/R group