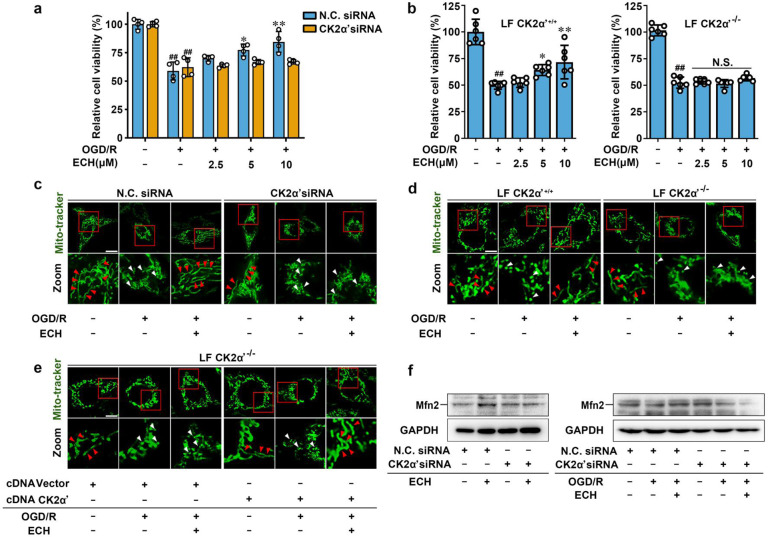
Fig. 3.
CK2α′ plays a fundamental role in modulating mitochondrial fusion. a CK2α′ knock-down reversed ECH-dependent increase in cell viability against OGD/R insult, which was detected by MTT assay. b ECH increased cell viability against OGD/R-induced injury in CK2α′+/+ lung fibroblasts, which was significantly suppressed in CK2α′−/− cells. c ECH-induced mitochondrial fusion was suppressed in CK2α′ knock-down cells, which was indicated by Mito-tracker staining. Arrows (red) indicate branched healthy mitochondria. Arrows (white) indicate spherical dysfunctional mitochondria (scale bar: 20 μm). d ECH-induced mitochondrial fusion was inhibited in CK2α′−/− cells, which was indicated by Mito-tracker staining. Arrows (red) indicate branched healthy mitochondria. Arrows (white) indicate spherical dysfunctional mitochondria (scale bar: 20 μm). e ECH recovered mitochondrial fusion induction in CK2α′−/− lung fibroblasts which were transfected with CK2α′ plasmid. Arrows (red) indicate branched healthy mitochondria. Arrows (white) indicate spherical dysfunctional mitochondria (scale bar: 20 μm). f Mfn2 expression induced by ECH was downregulated in CK2α′ knock-down PC12 cells, which was analyzed by western blot. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. ##P < 0.01 vs. control group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. OGD/R group. NS not significant