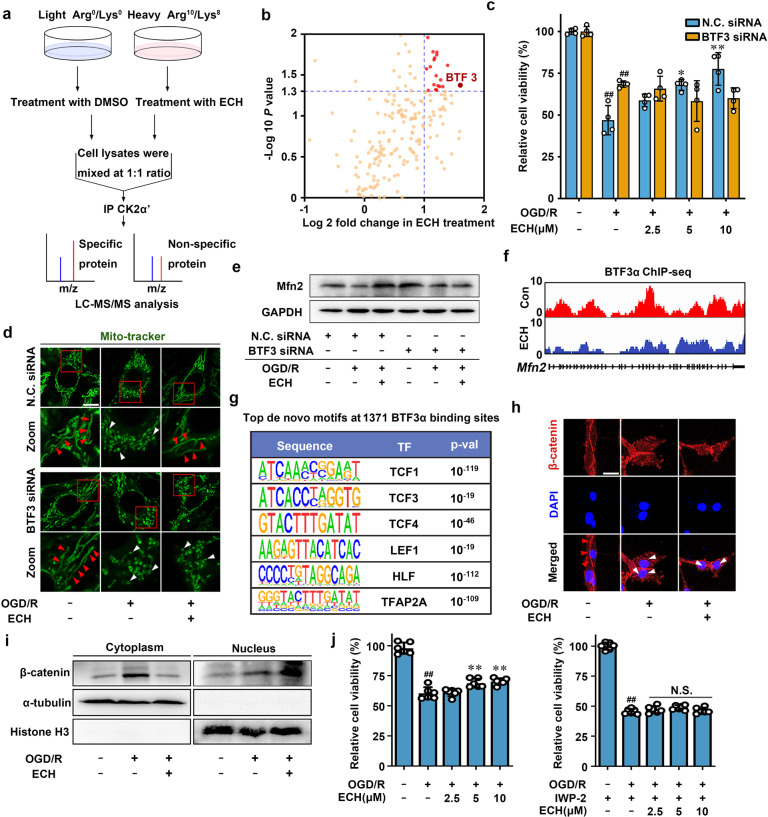
Fig. 4.
CK2α′ binds to basic transcription factor (BTF3) as a direct substrate. a Stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture (SILAC)-coupled pull-down technology was used to identify the binding substrates of CK2α′. b Overview of the binding substrates of CK2α′ was identified by LC–MS/MS. c BTF3 knock-down inhibited ECH-mediated cell viability increase, which was detected by MTT assay. d ECH-induced mitochondrial fusion was inhibited in BTF3 knock-down cells, which was indicated by Mito-tracker staining. Arrows (red) indicate branched healthy mitochondria. Arrows (white) indicate spherical dysfunctional mitochondria (scale bar: 20 μm). e BTF3 knock-down inhibited Mfn2 expression, which was detected by western blot. f Genome browser view of BTF3α ChIP-seq signal on Mfn2 gene loci. g Top enriched de novo transcription factor (TF) motifs within 14 bp upon ECH treatment. h Co-localization of β-catenin (red) and DAPI (blue) was detected by immunofluorescent staining. Arrows (red) indicate cytoplasmic location of β-catenin. Arrows (white) indicate nuclear translocation of β-catenin from the cytoplasm (scale bar: 20 μm). i ECH facilitated β-catenin nuclear translocation. j IWP-2 reversed ECH-dependent cell viability increase under OGD/R insult. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. ##P < 0.01 vs. control group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. OGD/R group