Figure 3.
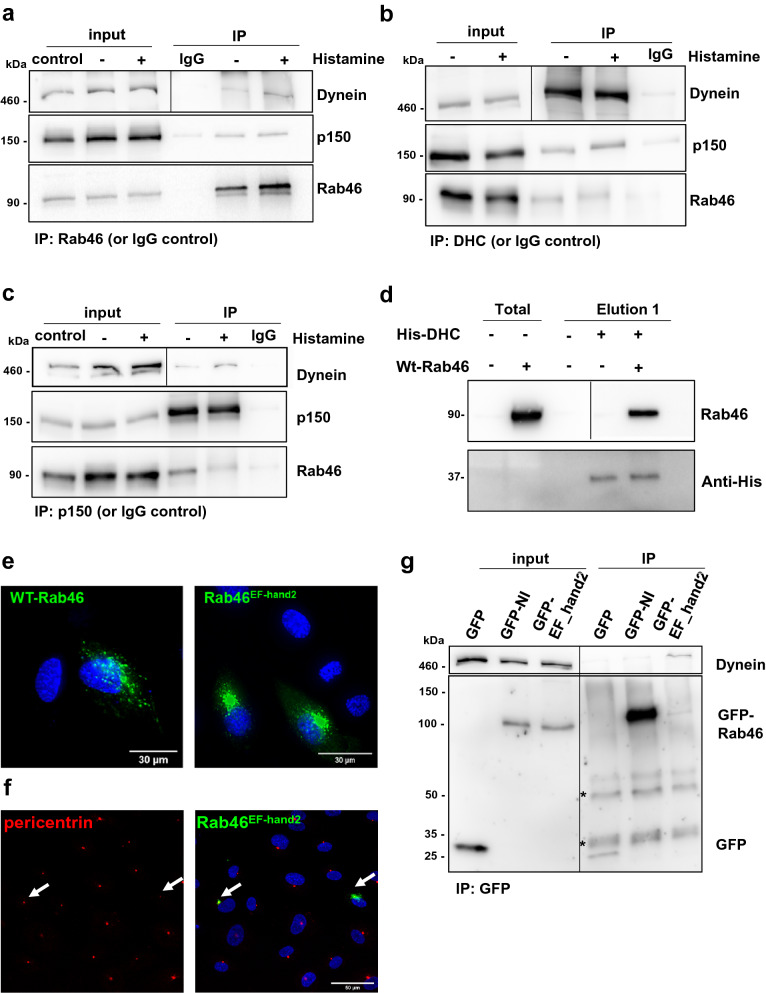
Rab46 interacts with the dynein/dynactin complex in a Ca2+ independent manner. a, b and c represent Co-IPs of endogenous Rab46 (a), DHC (b) and p150 (c). The input lanes represent the total amount of the proteins of interest in the lysate prior to IP and indicate loading. The lysates are from histamine, vehicle treated and control cells prior to pull down with either the named antibody or IgG isotype (control sample). (a) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of endogenous Rab46 in HUVECs stimulated with 30 μM histamine or vehicle was performed using an anti-Rab46 antibody and Co-IP of DHC and p150, subunit of dynactin, was assessed by immunoblotting. Note the interaction between dynein and Rab46 has been shown previously9. Here we show the interaction is part of a complex with p150. (b) Reverse Co-IP of endogenous Rab46 and p150 subunit was performed using anti-DHC antibody, Co-IP was assessed by immunoblotting for Rab46 and p150. (c) Reverse Co-IP of endogenous Rab46 and DHC was performed using anti-p150 antibody, Co-IP was assessed by immunoblotting. Input represents total lysate before the IP and samples after the IP are denoted as IP. Corresponding IgG were used as negative control. Blots are representative of 3 independent experiments. (d) Pull down of human WT-Rab46 overexpressed in Cos7 cells using purified his-tag DHC (His-DHC) bound to Ni2+ beads. Non-transfected cells (–) and cells transfected with WT-Rab46 (+) were mixed with (+) or without (–) 10 μg of His-DHC. Magnetic sepharose Ni2+ beads were used to pull-down His-tag DHC complexes: the beads were incubated with the mixture of His-DHC + WT-Rab46 (or non-transfected cells as control) or WT-Rab46 only as control to show non-specific binding to the beads. Pull down of Rab46 with his-DHC was assessed by western blot using anti-Rab46 and anti-histidine antibodies. Western blots are representative of 3 independent experiments. (e) Representative images of HUVECs expressing WT-Rab46 or Rab46 EF-hand2 mutant (green). Scale bar = 30 μm. (f) Deficiency in Ca2+ binding shows Rab46 EF-hand2 mutant clustering in the perinuclear area at the MTOC. Pericentrin (red: left image) acts as marker for the MTOC. Arrows depict cells where pericentrin (right and left images) and Rab46 EF-hand2 mutant (green) co-localise at the MTOC in the merged image (right). DAPI (blue) represents nuclei. Scale bar = 50 μm. g) Immunoprecipitation of Rab46 binding mutants (GFP-N658I and GFP-EF hand2 mutant) in HUVECs was performed using an anti-GFP antibody and Co-IP of DHC was assessed by immunoblotting for DHC. Input represents total lysate before the IP and samples after the IP are denoted as IP. Empty GFP vector was used as negative control. (*) indicates non-specific bands corresponding to the IgG heavy (50 kDa) and light chains (25 kDa). Note in all blots/IPs the black line delineates a cropped image. Raw images of membranes are available in Fig. S5.