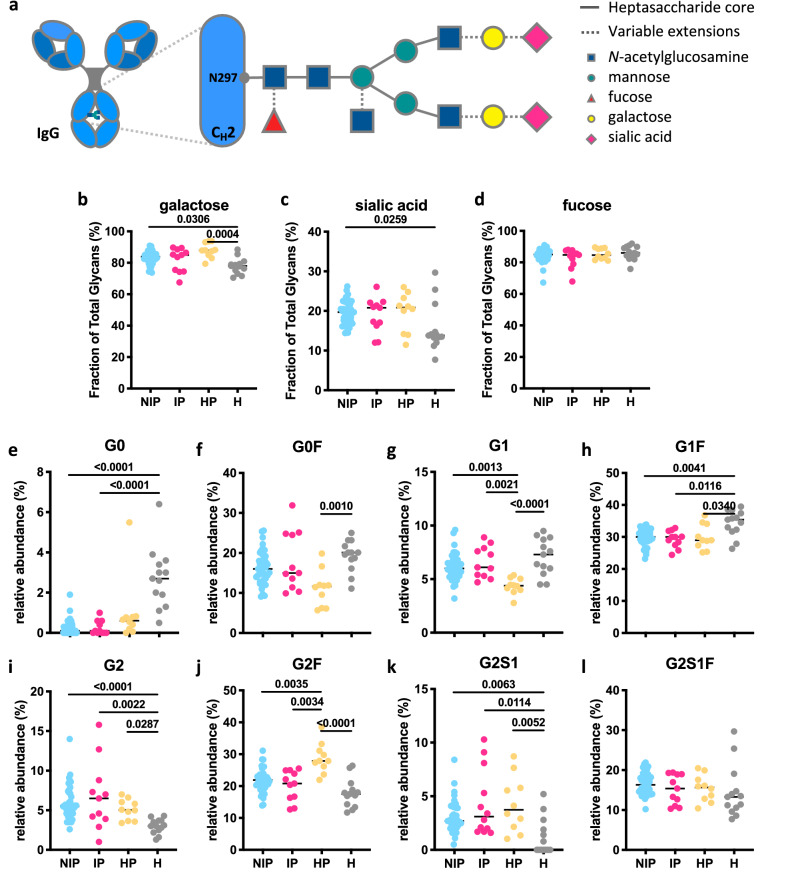
Figure 6.
Glycan profiles of IgG Abs in pregnant women with malaria. (a) Schematic representation of N-linked glycan composition of human IgG Abs. The glycans are attached to asparagine (N) at position 297 in the CH2 domain of IgG and have a biantennary heptasaccharide core (solid line) and variable extensions (dash line), such as fucose, galactose and/or sialic acid. Relative abundance of specific types of N-linked glycan structures of purified IgG Abs from non-infected pregnant women (NIP; N = 41; blue), pregnant women with malaria infection (IP; N = 11; pink), malaria-naïve healthy pregnant women (HP; N = 10; yellow) and uninfected healthy non-pregnant women (H; N = 13; grey) were profiled. % of Fc glycans with the presence of (b) galactose (monogalactosylated or digalactosylated), (c) sialic acid and (d) fucose. (e–l) The relative prevalence of several major glycan structures (G0 agalactosylated, G1 monogalactosylated, G2 digalactosylated, F fucosylated, S1 sialylated). Statistical comparison between groups was performed using a Kruskal–Wallis test corrected for multiple comparisons using Dunn’s multiple comparison method (p-values are shown on graphs).