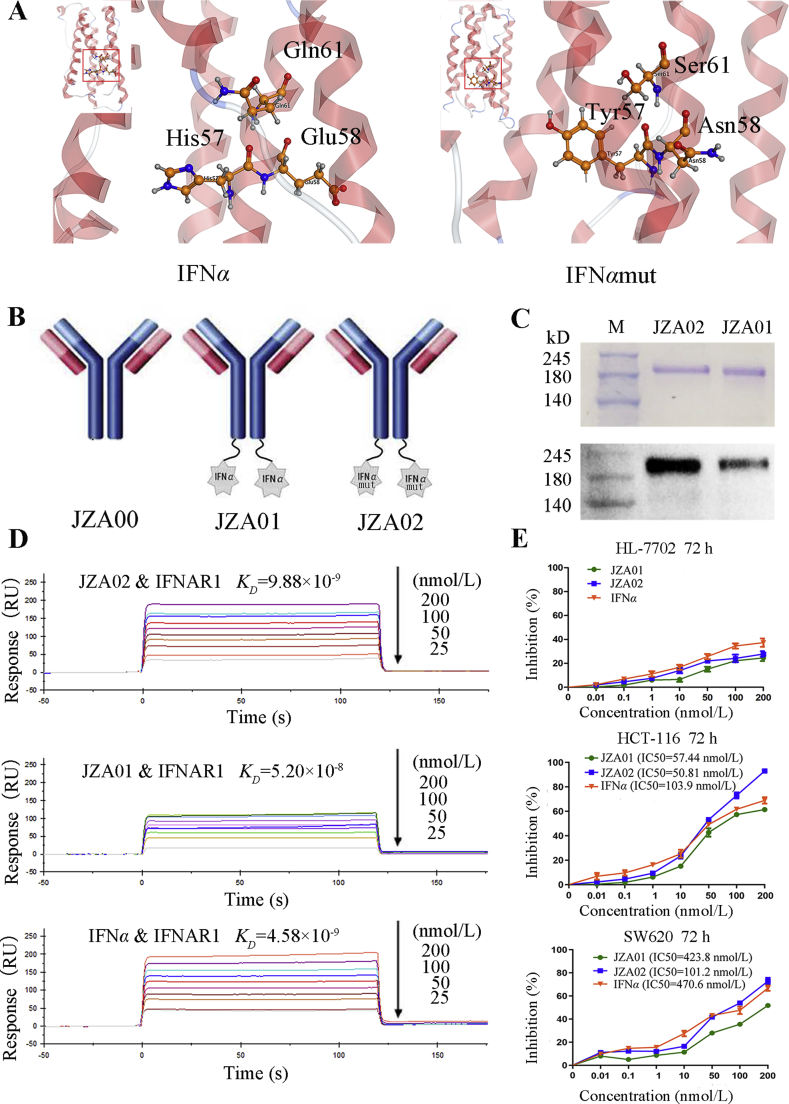
Figure 1.
Construction and characterization of JZA02. (A) 3-D structural model of IFNα and IFNαmut. MOE was be used to build the 3-D model of IFNα and IFNαmut. (B) Diagram of JZA01 and JZA02. IFNα or IFNαmut was linked to the C-terminal of the H-chain of JZA00 with a G4S linker using overlap PCR. (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of JZA02 followed by either Coomassie blue staining or Western blot analysis with anti-IFNα antibody show that it was intact and assembled properly. (D) The binding affinity of immobilized JZA02, JZA01, or IFNα with IFNAR1 was determined with the Biacore system. The association rate increased with increasing concentration of the IFNAR1 (from bottom to top), which ranged from 0.78125 to 200 nmol/L. The complex dissociated when buffer was flowed through for 120 s. (E) HL-7702 cells, HCT-116 cells, and SW620 cells were treated with varying concentrations of IFNα, JZA01, or JZA02 for 72 h, respectively, and a MTT assay was used to detect the surviving cells. Inhibition of proliferation was plotted relative to the proliferation of untreated controls which was set to 100%.