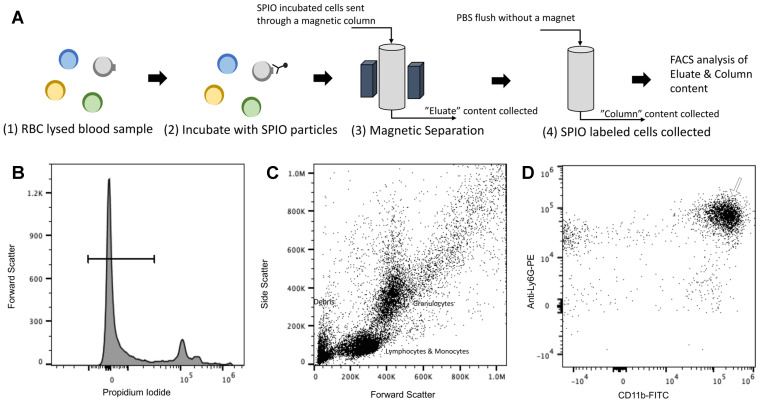
Figure 11.
Cell Enrichment Analysis of MPI tracers using Flow Cytometry (A) Cells obtained after RBC lysis of mouse blood were incubated with SPIO of interest. The incubated cells were sent through a magnetic column, and unlabeled cells were collected as “eluate” from the column. After removing the magnet utilized for separation, the column was further flushed, and the contents were collected as the “column” subset of cells. The immune cell population from the “eluate” was evaluated for degree of depletion by the SPIO relative to the extent to which it is enriched from the “column” in comparison with control (untouched RBC lysed blood) using flow cytometry. The following gating procedure was carried out on the flow cytometry data: (B) the propidium iodide channel was used to gate live cells, which are negative for the dye, (C) the granulocyte population of immune cells were chosen utilizing the side scatter and forward scatter profile and (D) the cells were analyzed for neutrophil cell marker expression (anti-Ly6G-PE and CD11b-FITC) utilizing the PE and FITC channels. Untouched (i.e. unseparated) samples of RBC lysed blood were used as a control to gauge the native proportion of blood cells in the samples (MPI: magnetic particle imaging; RBC: red blood cells; SPIO: superparamagnetic iron oxide).