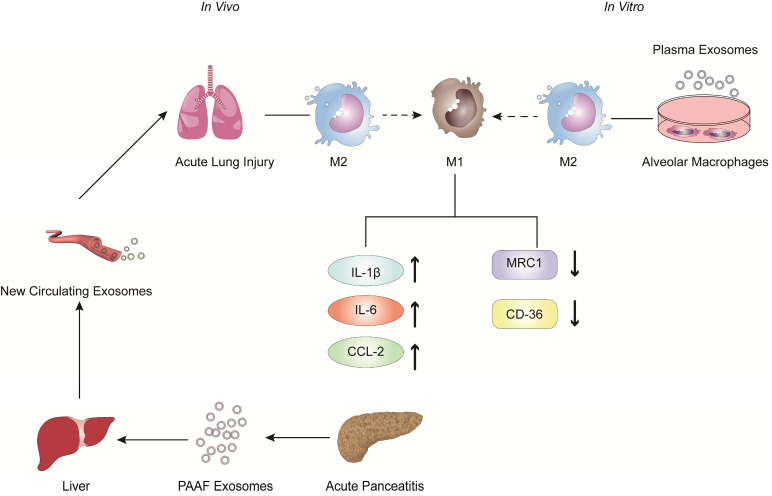
Figure 1.
The role of extracellular vesicles in the mechanism of AP-related alveolar macrophage activation. The figure shows that in vitro experiments (left) revealed that part of the PAAF exosomes released from the pancreas during AP entered the liver directly through the portal system, and most of them were retained in liver tissue. During AP, the formation of new circulating exosomes from the liver reached the alveoli and activated the alveolar macrophages from the M2 phenotype to the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype, leading to significantly increased expression of cytokines IL-1, IL-6 and chemokine CCL2, while the expression of MRC1 and CD36 was decreased. In vivo experiments (right) showed that plasma exosomes from AP promoted the activation of alveolar macrophages from the M2 phenotype to the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype, and resulted in significantly increased expression of the inflammatory cytokines IL-1 and the chemokine CCL2 in alveolar macrophages.