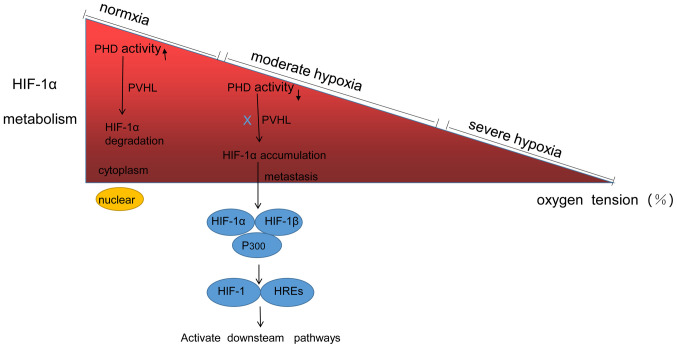
Figure 1.
HIF-1α metabolism. HIF-1 belongs to the Per-Arnt-Sim family, heterodimeric proteins composed of α and β subunits. Under normoxia, the α subunit is hydroxylated and subsequently activates PHD, which is then degraded HIF-1α via pVHL. However, the PHD activity is reduced during moderate and severe hypoxia, following which the degradation of the α subunit is inhibited, so HIF-1α gradually accumulates in the cytoplasm. HIF-1α then enters the nucleus and binds to HIF-1β to form an ectopic dimer, HIF-1, which recognizes and binds to HREs to activate the downstream target genes. HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; PHD, prolyl hydroxylase; HREs, hypoxia responsive elements; pVHL, protein von HippeI-Lindau.