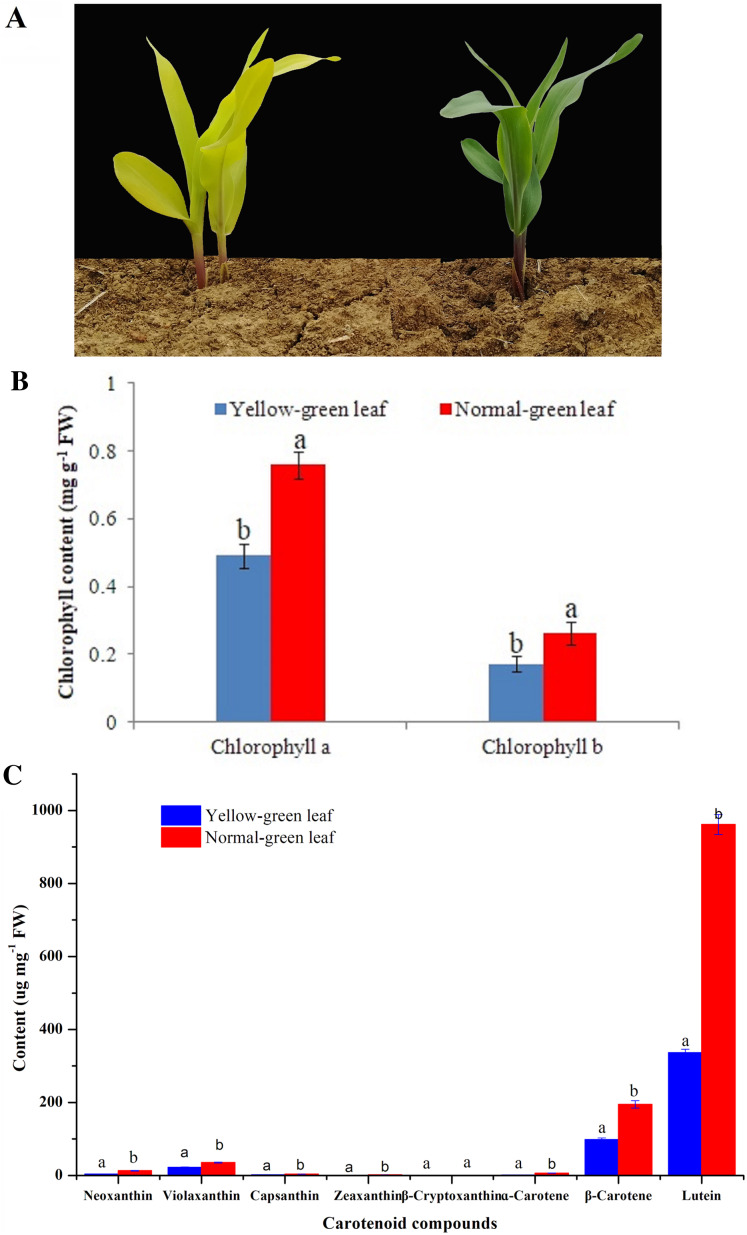
Figure 1. Phenotypic characteristics change of yellow-green leaf mutant plants.
(A) Indicated two yellow-green leaf mutant plants and a normal green leaf plant at the same age. Maize plants in this image were at the five-leaf stage. (B) Showed the contents of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b in the normal green leaf inbred line and the yellow-green leaf mutant. (C) showed the contents of eight carotenoid compounds including neoxanthin, violaxanthin, capsanthin, zeaxanthin, β-cryptoxanthin, ɑ-carotene, β-carotene and lutein. Small letters a and b above the columns indicate differences between the yellow-green leaf mutant and the normal green leaf inbred line at P < 0.05, according to least significant difference (LSD) tests. FW is the abbreviation of the fresh weight.