Figure 7.
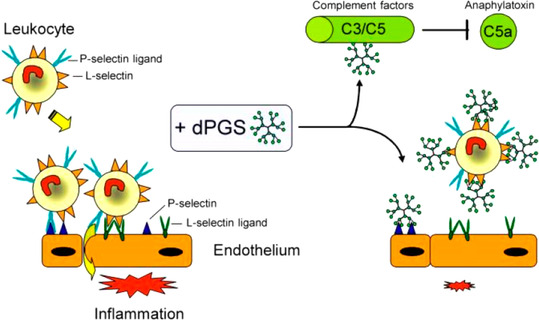
The anti‐inflammatory effect of dPGS. As shown by Dernedde et al., [36] dPGS inhibits an overwhelming inflammatory response and reduces the extravasation of leukocytes. dPGS targets the adhesion molecules L‐ and P‐selectin, while no binding to E‐selectin is observed. The same finding was made in our recent study by MD simulations. [45] Thus, dPGS acts by preventing leukocyte extravasation through the binding of the selectins. Moreover, binding to complement factors C3 and C5 inhibits the formation of the proinflammatory anaphylatoxins. Here, the reduction of the C5a level decreases further leukocyte activation and recruitment. As a result, the adhesion cascade is balanced and contributes to initiate the healing process. [196]
