Figure 1.
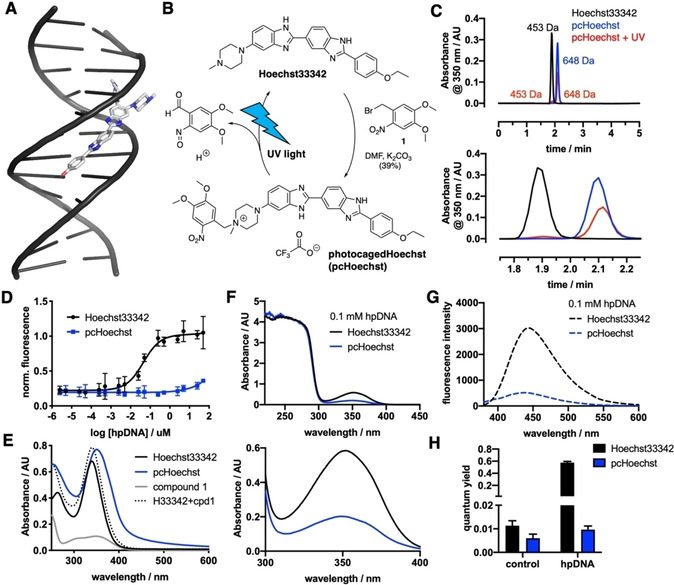
Synthesis and in vitro characterization of pcHoechst. A) Hoechst33258 binds to the minor groove of DNA (PDB ID: 8BNA), showing a disordered, partly solvent‐exposed piperazine. B) pcHoechst is obtained by benzylation of Hoechst33342 with an o‐nitro benzyl photocage that can be removed with UV light to re‐obtain Hoechst33342. C) Chromatograms of Hoechst33342, pcHoechst and a sample of pcHoechst that was irradiated for 5 min with white light show that the appearance of Hoechst33342 (top) matches the occurrence of Hoechst after pcHoechst irradiation by retention time and molecular weight (enlargement below). D) Concentration‐response curve for Hoechst33342 and pcHoechst against hairpin (hp) DNA. No fluorescence can be detected for pcHoechst. E) UV/Vis spectra of Hoechst33342, pcHoechst and o‐nitrobenzylbromide 1. Mathematical addition of Hoechst33342 plus compound 1 is drawn as a dashed line. F) UV/Vis spectra of Hoechst33342 and pcHoechst in the presence of 0.1 mM hpDNA (top) with enlargement (bottom). G) Fluorescence emission spectra of Hoechst33342 and pcHoechst in the presence of 0.1 mM hpDNA. H) Quantum yield measurements of Hoechst33342 and pcHoechst in the absence (control) and presence of 0.1 mM hpDNA.
