Figure 1.
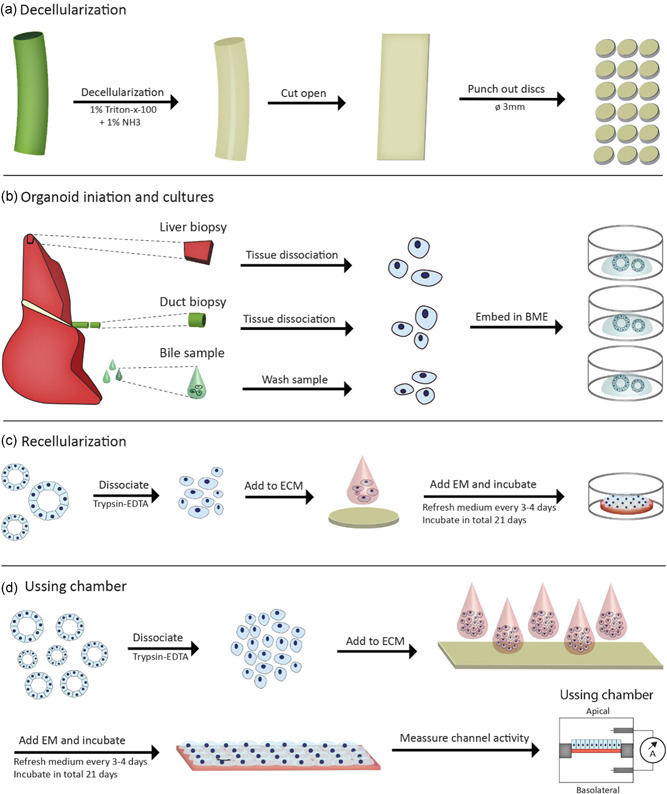
Graphical representation of human EBD decellularization and recellularization procedures. (a) Decellularization of EBD tissue was performed with T×100 solution. After decellularization the full length EBD was cut open along the longitudinal axis and circular discs (Ø3 mm) are punched using a dermal biopsy punch. (b) Organoids were initiated from three different sources; liver tissue (IDO), EBD tissue (EDO), and bile samples (BDO). The cells obtained from these sources were embedded in BME and cultured as per normal protocol. (c) Recellularization experiments start with dissociation of the organoids. A suspension of single cells (10 µl) was added to the ECM and kept in culture for up to 21 days. (d) Recellularization experiments for Ussing Chamber were performed in a similar manner as the normal recellularization experiments. After a 21‐day culture period, the recellularized construct was carefully placed inside the Ussing chamber setup, followed TEER and ion‐channel activity measurements in Ussing chambers. BDO, bile‐derived organoids; BME, basement membrane matrix; EBD, extrahepatic bile duct; ECM, extracellular matrix; EDO, extrahepatic bile duct‐derived organoids; IDO, intrahepatic bile duct‐derived organoids; TEER, trans epithelial electrical resistance [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
