Figure 1.
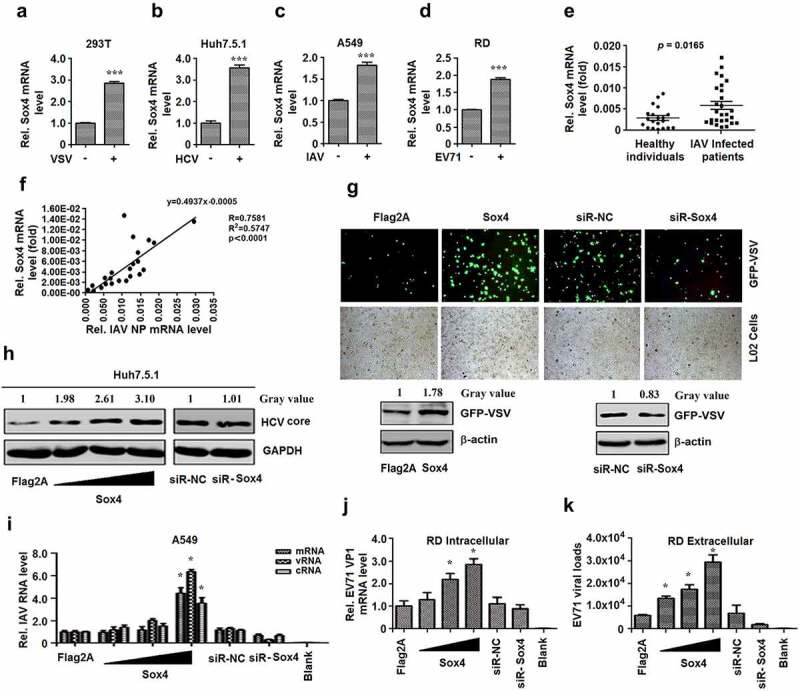
Viruses activate Sox4 expression, which subsequently facilitates viral replication. (A to D) 293 T cells were infected with VSV (a), Huh7.5.1 cells were infected with HCV (b), A549 cells were infected with IAV (c), RD cells were infected with EV71 (d). Sox4 mRNAs expressed in infected cells were detected by RT-PCR. (e and f) Sox4 mRNAs expressed in IAV-infected patients and healthy individuals were detected by RT-PCR (e). Sox4 and IAV NP mRNAs expressed in IAV-infected patients were detected by RT-PCR, and the correlations of Sox4 mRNAs and IAV NP mRNAs were analyzed (f). (g) Fluorescence micrographs of L02 cells infected with GFP-VSV and transfected with pFlag-Sox4 or siR-Sox4 (upper panel). Western Blot analysis the replication of GFP-VSV corresponding to the cells for acquiring micrographs by anti-GFP (lower panel). (h) Huh7.5.1 cells were infected with HCV and transfected with pFlag-Sox4 in a dose-dependent manner (left) or siR-Sox4 (right). HCV core proteins were detected by Western blots. (i) A549 cells were infected with IAV and transfected with pFlag-Sox4 or siR-Sox4. IAV NP mRNA, vRNA, and cRNA were analyzed by RT-PCR. (j and k) RD cells were infected with EV71 and transfected with pFlag-Sox4 or siR-Sox4. HCV VP1 mRNAs in the cell extractions (j) or culture supernatants (k) were determined by RT-PCR. Results are shown as means ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001
