Fig. 1.
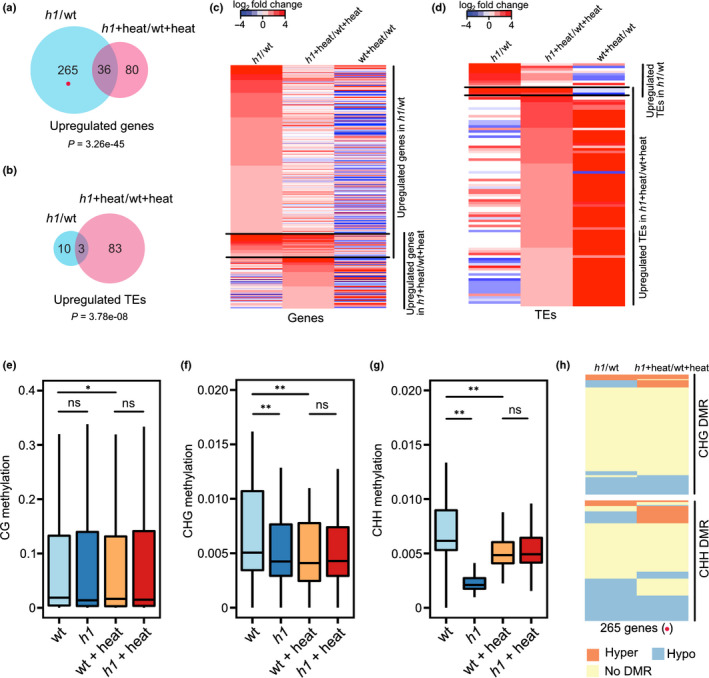
Histone H1 is required for transposable element (TE) repression after heat stress inArabidopsis. Venn diagrams show upregulated genes (log2‐fold change ≥ 1, adjusted P‐value (padj) ≤ 0.05, (a)) and TEs (log2‐fold change ≥ 1, padj ≤ 0.05, (b)) in h1 mutants vs wild‐type (h1/WT) and h1 plus heat vs WT plus heat (h1 + heat/WT + heat). The red dot in (a) represents the same group of genes marked in panel (h). Heat maps show upregulated genes (c) and TEs (d) in h1 mutants vs WT and h1 plus heats WT plus heat. Averaged CG (e), CHG (f) and CHH (g) methylation in the −2 kb to transcription start site (TSS) region of 265 upregulated genes in h1 mutants vs WT but not in h1 plus heats WT plus heat are shown in four different conditions of WT, h1, WT plus heat (WT + heat), and h1 plus heat (h1 + heat). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ns, not significant (Wilcoxon test). The lower and upper hinges of the boxplots correspond to the first and third quartiles of the data, the black lines within the boxes mark the median. CHG and CHH DMRs (h) in the −2 kb to TSS region of 265 upregulated genes in h1 vs WT. Hyper and hypo refer to hyper‐ or hypomethylated regions, respectively, present in the upstream region of genes in h1 vs WT or h1 plus heat vs WT plus heat.
