FIG. 8.
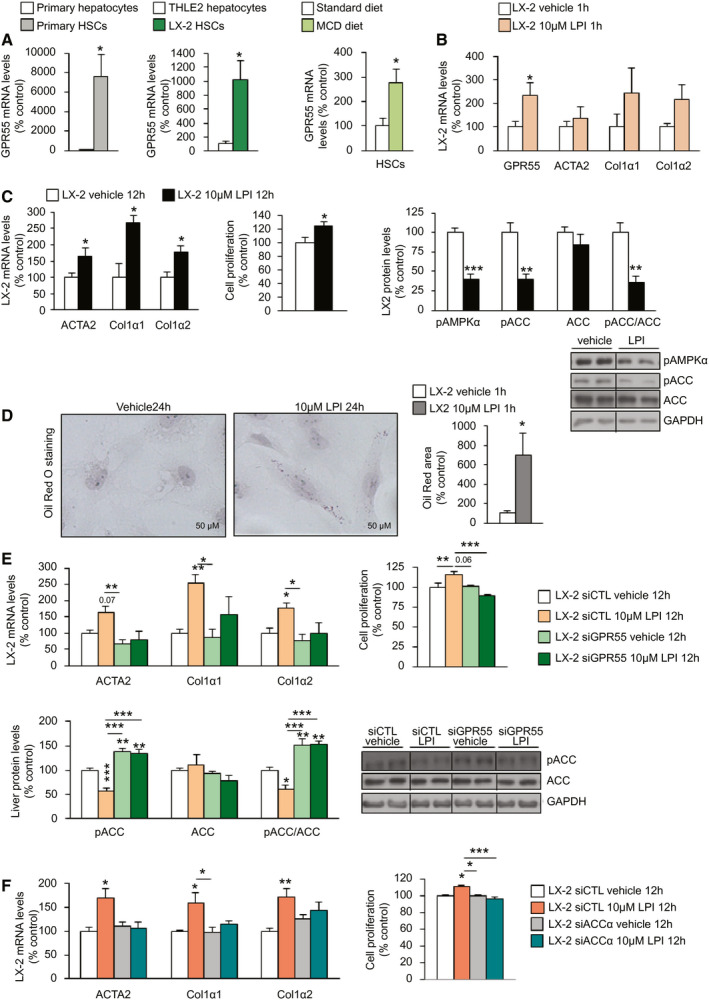
LPI activates LX‐2 HSCs through GPR55 and ACC. (A) GPR55 mRNA levels in primary HSCs compared with primary hepatocytes obtained from mice fed a standard diet and in LX‐2 human HSCs compared with THLE2 cells (n = 4‐8); HSCs isolated from the liver of mice fed an MCD diet or a standard diet for 4 weeks (n = 2‐4). (B) GPR55, ACTA2, COL1α1, and COL1α2 mRNA expression in LX‐2 cells after the administration of LPI (n = 8). (C) ACTA2, COL1α1, and COL1α2 mRNA expression; relative proliferation measured by MTT test; and protein levels of pAMPKα, pACC, and ACC in LX‐2 cells treated with LPI or vehicle for 12 hours (n = 6‐12). (D) Oil Red O staining of LX‐2 cells showing staining of lipids after the administration of LPI for 24 hours (n = 6). The right graph shows total lipid content normalized to the total number of nuclei per field. (E) ACTA2, COL1α1, and COL1α2 mRNA expression and relative proliferation and protein levels of pACC and ACC in LX‐2 cells transfected with siGPR55 or scrambled siRNA and treated with 10 µM LPI or vehicle for 12 hours. (F) ACTA2, COL1α1, and COL1α2 mRNA expression and relative proliferation in LX‐2 cells transfected with siACCα or scrambled siRNA (n = 6) and treated with vehicle or LPI for 12 hours. HPRT and GAPDH were used to normalize mRNA and protein levels, respectively. Dividing lines indicate spliced bands from the same gel. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical differences are denoted by *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. Abbreviations: ACC, acetyl–coenzyme A carboxylase; ACTA2, actin α2; COL1α1, collagen α1; COL1α2, collagen α2; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; GPR55, G protein–coupled receptor 55; HPRT, hypoxanthine‐guanine phosphoribosyltransferase; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; LPI, l‐α‐lysophosphatidylinositol; MCD, methionine‐choline–deficient; MTT, 3‐(4,5‐dimethylthiazol‐2‐yl)‐2,5‐diphenyltetrazolium bromide; pACC, phosphorylated ACC; pAMPKα, phosphorylated adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase α; siACCα, siRNA ACCα; siCTL, siRNA control; siGPR55, siRNA GPR55; siRNA, small interfering RNA.
