Abstract
Since the discovery that the so‐called “double‐bond” rule could be broken, the field of molecular main group multiple bonds has expanded rapidly. With the majority of homodiatomic double and triple bonds realised within the p‐block, along with many heterodiatomic combinations, this Minireview examines the reactivity of these compounds with a particular emphasis on small molecule activation. Furthermore, whilst their ability to act as transition metal mimics has been explored, their catalytic behaviour is somewhat limited. This Minireview aims to highlight the potential of these complexes towards catalytic application and their role as synthons in further functionalisations making them a versatile tool for the modern synthetic chemist.
Keywords: bond activation, catalysis, main group, multiple bonds, small molecule activation
The versatile reactivity of molecular main group multiple bonds is covered in this Minireview, from small molecule activation to catalysis and to their role as synthons in further functionalisation reactions.
Introduction
Molecular main group multiple bond chemistry has rapidly developed since the isolation of the first silicon‐silicon double bond. West's disilene [1] broke the so called “double‐bond” rule, in which it was thought that p‐block elements with a principal quantum number greater than two (i.e. aluminium onwards) would not form multiple bonds with themselves or other elements. Seminal examples, all from 1981, reported by West (Si=Si), Yoshifuji (P=P), [2] Brook (Si=C), [3] and Becker (P≡C) [4] paved the way for this new field. Almost 40 years on, homodiatomic double bonds have now been isolated for all p‐block elements in groups 13–15, rows 2–6.[ 5 , 6 , 7 ] Extension to homodiatomic triple bonds is complete for group 14, whilst only one clear example of a group 13 triple bond exists. [8] Further advances in heterodiatomic multiple bonding for p‐block elements has yielded many new complexes, yet several still remain elusive.
Synthetic challenges in main group multiple bond chemistry have largely been overcome through choice of supporting ligand. Careful design of sterically demanding ligands is required in order to provide sufficient kinetic stabilisation to the multiple bond (Figure 1). If too small higher oligomers are obtained or if too large steric clash will prevent multiple bond formation. For example, on increasing the steric demands of phenyl to mesityl (mesityl=2,4,6‐trimethylphenyl) multiple bond formation is achieved (Compounds 1 [9] vs. 2, [1] Figure 1). Similarly, the widely studied tetrameric pentamethylcyclopentadiene (Cp*) aluminium complex (3) [10] dissociates into its monomeric form at elevated temperatures. It was only recently, however, that a monomeric Cp‐derived AlI species was isolated (4) [11] through increasing the steric demands of the substituents. It is of note, that no dimeric (i.e. multiple bond) structure has been observed for the aluminium Cp systems.
Figure 1.
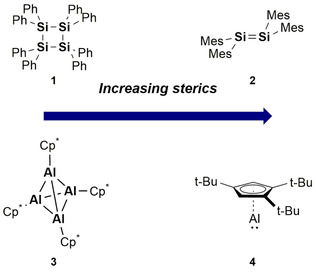
Effect of ligand steric demands on isolable structures. Mes=2,4,6‐trimethylphenyl, Cp*=1,2,3,4,5‐pentamethylcyclopentadienyl.
On descending the group the stability of the lower oxidation state increases and thus its desire to partake in bond formation decreases. For example in group 14, SnII is more stable than SnIV, whilst for the lightest congener CIV is more stable than CII. This can also influence the complex formation in both the solution and solid state as highlighted by Lappert's stannylene. The use of a bis(trimethylsilyl)methyl ligand (CH(SiMe3)2) provides sufficient kinetic stabilisation to isolate a two‐coordinate SnII compound, however in the solid state this exists as a dimer yielding a Sn=Sn multiple bond.[ 12 , 13 ]
One of the reasons for the rapid development of main group multiple bonds is due to their ability to act as transition metal mimics. Owing to similarly energetically accessible frontier orbitals, main group multiple bonds have been shown to activate small molecules, such as dihydrogen, under ambient conditions (Figure 2).[ 14 , 15 ] This often results in an oxidative addition reaction occurring at the main group centre. However, unlike transition metals, reductive elimination at main group centres is more challenging due to the resulting high stability of the M(n+2) oxidation state, particularly for the lighter, more earth abundant elements such as aluminium and silicon. This impedes the catalytic ability of main group metals in traditional redox based cycles as turnover is not possible. This also applies to main group chemistry in general, however alternative catalytic processes have been utilised which circumvent the change in oxidation state. These non‐redox processes typically involve a series of σ‐bond metathesis/insertion steps to enable turnover. [16]
Figure 2.
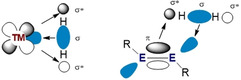
Frontier molecular orbitals of transition metals (left) and main group multiple bonds (right) for the activation of dihydrogen.
Multiple bonds offer an attractive tool for the main group chemist due to the presence of a metal‐metal bond. Metal–metal bonds from across the periodic table bonds have enabled a series of unique bond activations and catalysis, particularly in transition metal chemistry [17] and f‐elements. [18] In transition metal chemistry, metal–metal bonds have broad applications and have been found to play key roles in catalytic processes. [17] The use of transition metal multiple bonds in catalysis has allowed for retention of the dinuclear complex on addition of the substrate (Scheme 1 A). They have also found roles as pre‐catalysts, providing access to a monomeric low valent “active” species (Scheme 1 B).
Scheme 1.
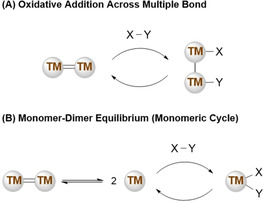
Generic catalytic cycles for the activation of substrates (X–Y) by transition metal multiple bonds.
Both above‐mentioned steps within a catalytic process could be envisioned for main group multiple bond chemistry, yet their use in catalysis is currently limited to just two examples. A digermyne, a germanium‐germanium triple bond, which was used for the cyclotrimerisation of terminal alkynes [19] and a dialumene, an aluminium–aluminium double bond, which was found to be an active pre‐catalyst for the reduction of carbon dioxide. [20] These two examples show the potential for this field to offer an alternative to expensive and often toxic transition metals that are currently used in industry. In addition to main group multiple bonds, low oxidation state and/or coordinate main group complexes have also undergone a renaissance in recent years. With several new breakthroughs revealing new classes of compounds, such as nucleophilic aluminyls,[ 21 , 22 ] as well as advances in bond activations and catalysis.[ 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ] The synthesis and bonding nature of main group multiple bonds have been reviewed recently.[ 5 , 6 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 ] This minireview, therefore, focusses on the reactivity of these compounds highlighting the unique transformations that can be achieved due to molecular main group multiple bonds.
Group 13 Multiple Bonds
E13–E13 multiple bonds
Historically it was thought that group 13 elements (E13) would preclude multiple bond formation. The presence of only 3 valence electrons, as well as weak E13−E13 bond energies, leads to a high tendency for decomposition and disproportionation reactions. One successful method to overcome these challenges is to use Lewis bases to help stabilise the multiple bond, through donation of a lone pair into the vacant E13 p‐orbital. Owing to their easily tuneable steric and electronic properties, NHCs have a proven track record in main group chemistry, [34] and have enabled the isolation of the first diborene (5), [35] diboryne (6) [8] and dialumene (7) [7] (Figure 3). As expected for lighter elements these complexes exhibit planar geometries. On descending the group, the stability of the lone pair increases, and Lewis base stabilisation is no longer required. The three‐coordinate trans‐bent double bonds can be stabilised using sterically demanding terphenyl ligands (Compounds 8–10, Figure 3).[ 36 , 37 , 38 ] Recent reviews have highlighted the different synthetic methodologies and alternate ligand choices for the formation of these electron precise multiple bonds, and as such will not be discussed herein.[ 29 , 39 , 40 ]
Figure 3.
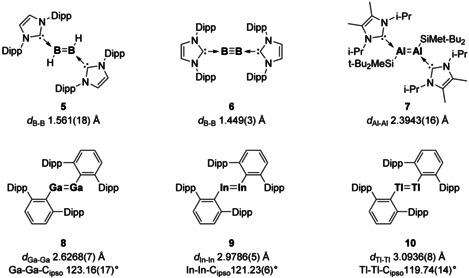
Selected examples of E13–E13 multiple bonds. Dipp=2,6‐di‐iso‐propylphenyl.
In terms of their reactivity, homonuclear E13 bonds have found themselves to be efficient tools for small molecule activation. For the lightest element, the reactivity of diboryne compounds were found to be influenced by the π‐acceptor ability of the supporting ligand.[ 41 , 42 , 43 ] CO coupling was observed for NHC‐stabilised complex (6) however these were unable to activate dihydrogen (Scheme 2 a). Switching to cyclic alkyl amino carbene (cAACs) ligands, which have increased π‐acceptor abilities relative to NHCs, enables diboryne (12) activation of dihydrogen at room temperature (13) but only coordination of CO was observed (14, Scheme 2 b). Additionally, NHC‐stabilised diborenes are able to fixate CO2 via [2+2]‐cycloaddition. The CO2 fixated compound was found to be thermally unstable and rearranged at room temperature through C−O cleavage and loss of the B−B bond to form a bridging carbonyl species. [44]
Scheme 2.
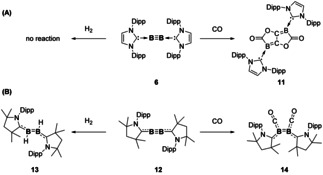
Ligand controlled small molecule activation with diborynes.
In a similar fashion, the NHC‐stabilised dialumene (7) was also found to fixate CO2. [20] In contrast to the diborene system, the CO2 fixation product was found to be stable and underwent further reactivity in the absence (carbonyl formation) or presence (carbonate formation) of additional CO2. The ability to access this carbonate species was found to be pivotal in the catalytic reduction of CO2. Catalytic reduction could be achieved with the addition of pinacol borane (HBpin). The mechanism for this was probed computationally (Scheme 3). It was found that dialumene (7) acts as a pre‐catalyst which forms carbonate 15 upon addition of CO2. Reduction by HBpin occurs at the exocyclic carbonyl to yield 15 a. CO2 then inserts into the bottom side of the Al–Al line of centres. The resultant eight‐membered ring (15 b) collapses with release of the formic acid equivalent, regenerating 15 in the process. Whilst this catalytic cycle does not contain an Al‐Al bond, the dinuclear complex remains intact due to bridging oxo and carbonate units and the ability of this system to alternate between reduction and insertion on the different sides of the Al–Al line of centres.
Scheme 3.
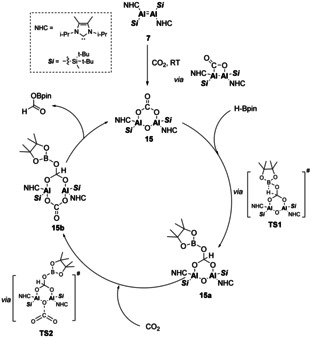
Proposed catalytic cycle for CO2 reduction by dialumene (7).
Very recently, a second neutral NHC‐stabilised dialumene (16) was isolated. [45] This differed to compound 7, due to the use of an aryl supporting ligand, which resulted in a trans‐bent and twisted geometry. The influence of the different ligands on the dialumene geometry was largely the result of the steric demands of the ligand. In terms of the electronics, the silyl ligand results in an almost neutral Al2 core whilst the aryl dialumene core is highly polarised, which can be attributed to the relative differences in electronegativities. Notably, this results in a much more reactive dialumene and reactivity towards sterically more demanding substrates is now possible due to the increased flexibility in the trans‐bent and twisted structure. Furthermore, facile activation of dihydrogen is now achievable (previously 7 showed no reactivity), yielding both the cis and trans‐isomers of a 1,2‐dihydro‐dialumane (17, Scheme 4). The influence of ligand choice is further implicated in two different catalytic reactions, namely hydroboration of CO2 and amine‐borane dehydrocoupling. The aryl‐stabilised dialumene (16) is more catalytically active and results in different product distributions. Thus, indicating the likelihood of alternate mechanisms simply through change of supporting ligand.
Scheme 4.
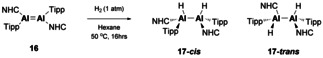
Dihydrogen activation by an aryl‐stabilised dialumene (16). Tipp=2,4,6‐tri‐iso‐propylphenyl.
Reactivity of heavier E13 multiple bonds (Ga‐Tl)[ 36 , 37 , 38 ] are limited to a few examples. Digallene (8) is capable of activating dihydrogen and ammonia [46] whilst dithallene (10) readily dissociates to its monomeric form in hydrocarbon solutions and therefore acts as a Lewis base in the formation of donor‐acceptor complexes. [38] Further reactivity studies of digallene show that whilst it can dissociate to its monomeric species it is in fact the double bond that is responsible for the observed reactivity.[ 47 , 48 , 49 ] The chemistry of homonuclear E13 multiple bonds is still in its infancy, with the potential for these systems far from fully realised. Boron is capable of forming stable triple bonds with itself, whilst aluminium [50] and gallium [51] have been isolated as anionic species, thus making their true bond order challenging to define. Extension to heteronuclear multiple bonding is also limited within E13. Currently, there is one example of a E13–E13’ multiple bond, a few examples of E13‐E14 and E13‐E15 multiple bonds and several E13–E16 multiple bonds. Again, this is due to difficulties within the synthesis and stabilisation of these inherently reactive species.
E13–E13′ multiple bonds
The first, and currently only, group E13‐E13’ complex which contains multiple bond character, was reported by Braunschweig and co‐workers (Compound 18, Scheme 5). [52] The resultant cAAC stabilised B‐Al bond is best described as a 3‐centre‐2‐electron π‐bond as DFT analysis found the HOMO to contain conjugation across the Al‐B‐cAAC unit. This bonding situation had been previously observed in related cAAC stabilised B−CO or B−N2 complexes.[ 53 , 54 ] 18 was also found to be efficient in small molecule activation as reaction of 18 with CO2 resulted in C−O and B−Al cleavage to form a borylene CO complex and an aluminoxane, compounds 19 and 20, respectively (Scheme 5).
Scheme 5.
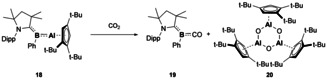
CO2 reduction by a boron‐aluminium multiple bond.
E13–E14 multiple bonds
Examples of group E13–E14 multiple bonds are also limited to a handful of examples and as such the reactivity of these compounds is largely unknown. Attempts to isolate borasilenes, that is compounds containing B=Si double bonds, have been achieved through matrix isolation techniques. [55] To date, only one neutral borasilene (21) [56] and one Lewis base stabilised borasilene (25) [57] exist in the condensed phase. Reactivity studies of 21 towards chalcogens revealed the formation of three‐membered rings with sulfur (22) and selenium (23), whilst with oxygen (24) a four‐membered ring, with loss of the B−Si bond, was found (Scheme 6 a). [58] The bonding situation in the Lewis base stabilised borasilene (25), based on experimental solid‐state structural features and DFT calculations, suggest 25 is best described as a zwitterionic double bond in contrast to borasilene 21. A series of resonance structures can be drawn (Scheme 6 b) with 25A, wherein the positive charge is located on the boron atom, representing the major resonance form. Attempts to use compound 25 for small molecule activation revealed no reactivity towards dihydrogen and an ill‐defined mixture with CO2. However, B−Si cleavage was observed on addition of HBpin, to yield BH2 and Si(Bpin)2 containing species. [57]
Scheme 6.
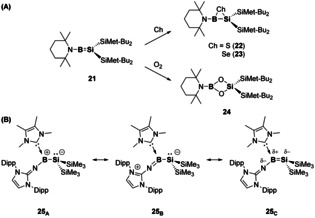
(a) Reactivity of borasilene (21) towards chalcogens. (b) Selected resonance structures of Lewis base stabilised borasilene (25).
E13–E15 multiple bonds
E13–E15 (pnictogen) multiple bonds are of interest to both academia and industry due to their interesting materials properties. Boron nitrides are widely used in the ceramics industry due to their high thermal and chemical stability, [59] whilst AlN, GaN, InN have interesting electronic properties. [60] Attempts to isolate discrete M=NR complexes has found limited success. Due to the necessity of sterically demanding ligands, the M=NR moiety is kinetically protected and therefore the reactivity of these compounds is somewhat impeded. To date, amongst the structurally characterised examples of E13 imides (E13=NR, E13=Al,[ 61 , 62 , 63 ] Ga,[ 64 , 65 , 66 ] and In[ 66 , 67 ]) only a few have reported further reactivity. Both Al and In imides (compounds 28 and 29, respectively) were synthesised from the corresponding E13(I) nucleophiles (Al 26; In 27) on reaction with MesN3 (Mes=2,4,6‐tri‐methylphenyl) (Scheme 7). In terms of their reactivity, the indium analogue undergoes further reactivity with organic azides to yield four membered rings (Scheme 7, compounds 30, 31). [67] Whilst the aluminium imide shows further reactivity with CO2 via a [2+2]‐cycloaddition to yield a carbamate dianion (Scheme 7, compound 32). [62]
Scheme 7.
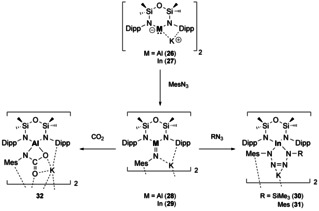
Reactivity of E13‐imides towards CO2 (Al only) and organic azides (In only).
In related work Aldridge, Goicoechea and co‐workers also obtained an Al imide complex (34) from reaction of their aluminyl ion (33) with DippN3 (Scheme 8). [63] The highly polar nature of the Al−N bond was highlighted through its reactivity with small molecules. Dihydrogen was found to add in a 1,2‐fashion across the Al−N bond at elevated temperatures (80 °C) to yield an amido aluminium hydride complex (35). Whilst two molecules of CO were found to react with 34 to yield compound 36 which is the result of C−O cleavage and C−C bond formation. [63]
Scheme 8.
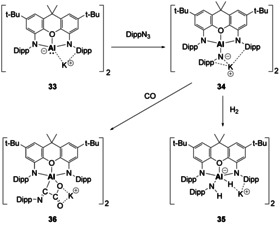
Synthesis and reactivity of an Al‐imide (34) towards small molecules.
Descending further down the pnictogen series, a few examples of Lewis acid or based stabilised B=P bonds exist, as well as B=As bonds.[ 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 ] Reactivity of these multiple bonds is scarce, but they have shown that they can be used as reagents to access C−C/P−B isoteres (Scheme 9). [72] Compound 37 was found to dissociate at elevated temperatures to provide the phosphaborene (38) in solution, this then undergoes [2+2]‐cycloaddition with phenylacetylene to yield compound 39. The ring opening reaction can be promoted through use of Lewis acids and bases to yield compounds 40 and 41, respectively. [72] Further reactivity of 38 showed that it could be used to access mixed main group element rings (Compounds 42 and 43, Scheme 9). [73]
Scheme 9.
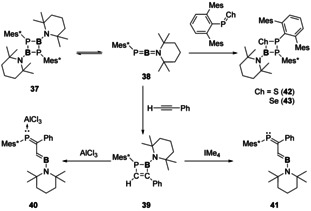
Phosphaborenes as a synthetic reagent. Mes=2,4,6‐trimethylphenyl; Mes*=2,4,6‐tri‐tert‐butylphenyl. IMe4=1,3,4,5‐tetramethyl‐imidazol‐2‐ylidene.
E13–E16 multiple bonds
E13–E16 (chalcogen) bonds are also of high interest due to their materials properties. For example, alumina has found widespread use in industry from heterogenous supports to materials and even cosmetics. [74] The inert nature of alumina arises from the large differences in electronegativities (Al 1.61, O 3.44) which results in a thermally stable material with high electrical resistance. The highly polarised bonds, however, also increase the difficulty of isolating a discrete E13=E16 multiple bond. As such, additional Lewis acid and base stabilisation is often required to stabilise the terminal E13=E16 bond (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
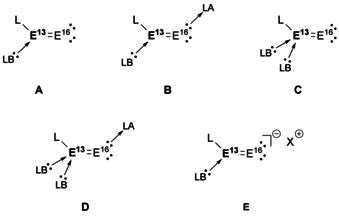
Different Lewis acid and base strategies for stabilisation of terminal E13=E16 multiple bonds.
The synthesis and isolation of E13–E16 multiple bonds have been highlighted recently,[ 40 , 75 ] and as such only recent progress in terms of their reactivity will be discussed herein. There have been significantly more reports of boron multiple bonds to chalcogens than any other E13 elements, including the only example of E13≡E16 triple bond. [76] Aldridge and co‐workers, recently reported the isolation of anionic oxoborane (44), [77] which is stabilised akin to type E in Figure 4. This compound can undergo π‐bond metathesis with CS2 to yield the related anionic thioxoborane. Furthermore, 44 was shown to act as an oxygen transfer agent (Scheme 10). Utilising a similar approach to Betrand, where the isoelectronic phosphinonitrene can act as a nitrogen transfer agent, [78] 1,3‐di‐p‐tolylcarbodiimide was added to 44 to yield 45. Addition of oxalyl chloride released the functionalised cyclic urea derivative with concomitant formation of the boron‐chloride species (46). Compound 44 could then be regenerated in a step wise manner through conversion to the boronic acid species (47), followed by deprotonation in the presence of a K‐sequestering cryptand ligand (Scheme 10). [77]
Scheme 10.
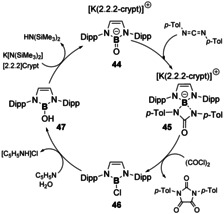
Step‐wise synthetic cycle for oxide ion transfer agent, 44.
A similar approach to the stabilisation of Al−O bonds was undertaken (Figure 4, type E). Again starting from the corresponding anionic AlI nucleophiles (26 and 33), reaction with 1 equiv. of N2O results in the formation of monoalumoxane anions (Scheme 11, 48 [79] and 49 [80] ). These are thought to contain some multiple bond character however, it is dominated by the anionic resonance form. [79] In the presence of additional N2O, five membered heterocycles are formed (50 and 51). These can either be isolated from the stepwise approach (via compounds 48 and 49) or via reaction of the nucleophilic starting materials (26 and 33) with excess N2O. A similar strategy can also be employed to access aluminium carbonate species (52 and 53), direct reaction of excess CO2 with the AlI nucleophiles results in carbonate formation with loss of CO. Also, the reaction of monoalumoxanes (48 and 49) with CO2 results in the direct insertion of the C−O bond into Al−O bond to yield the corresponding carbonates (52 and 53). Sequestering the potassium ion in 48 with [2,2,2‐cryptand], resulted in formation of a hydroxy species due to C−H activation of the iso‐propyl methyl of the flanking aryl group. Whilst reaction of 49 with dihydrogen yields an aluminium hydride hydroxy complex. This indicates the high Lewis basicity of the oxide anion in alumoxanes.
Scheme 11.
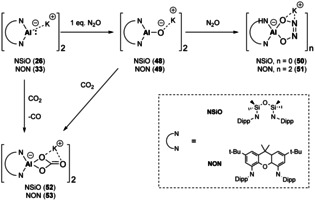
Synthesis and reactivity of monoalumoxanes.
The reactivity of 48 towards CO was examined to provide some insight into formation of an ethenetetrathiolate species, which was obtained from the reaction of 26 with CS2. [81] It was postulated that use of 48 would allow for isolation of intermediates due to the increased Al−O bond strength in comparison to Al−S (bond dissociation energies (BDE): 501 kJ mol−1 vs. 332 kJ mol−1, respectively). Addition of CO to 48 resulted in C−C bond formation in the form of the analogous ethenetetraolate ligand (54, Scheme 12). Mechanistic insights were provided by DFT calculations and highlighted the importance of the potassium counterion in this reaction, as several stabilising interactions from K+ were found in this transformation. [81]
Scheme 12.
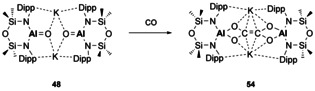
Synthesis of ethenetetraolate ligand (54).
Reactivity studies with the heavier aluminium chalcogenides is limited. Coles reported the selenium analogue to 48, which was synthesised in the presence of a cryptand ligand to sequester the cation (55, Scheme 13 a), [82] whilst in the absence of the cryptand a polymeric Al−Se species was obtained. Addition of a second equivalent of selenium to 55 affords a planar three‐membered AlSe2 ring (56). Evidence for the high degree of polarity in E13‐E16 bonds is shown by the Lewis base stabilised Al=Te complex (57). [83] This monotopic compound readily dimerises to 58, with loss of one Lewis base, on mild heating (Scheme 13 b). Whilst there are a few examples of Ga and In chalcogenide multiple bonds,[ 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 ] no onwards reactivity of these compounds has been reported. Heavier E13–E16 organometallic containing complexes, however, find themselves to be useful single source precursors for materials applications. [60]
Scheme 13.
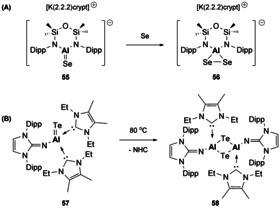
Reactivity of heavier aluminium chalcogenides.
Group 14 Multiple Bonds
E14–E14 multiple bonds
Of the main group multiple bonds, E14 elements are the most widely studied. For the lightest E14 member, carbon, its multiple bonds with itself and other elements account for the majority of known multiple bonds in existence, both those occurring naturally and synthetically. [88] In contrast, heavier E14 multiple bonds have only come to fruition in the last 40 years, starting with West's disilene. [1] Since then a plethora of E14=E14 double bonds have been isolated and been the subject of numerous reviews.[ 5 , 6 , 29 , 89 , 90 , 91 , 92 ] With their 4 valence electrons, triple bond formation is much more facile in comparison to E13 and disilynes (59), [93] digermynes (60), [94] distannynes (61) [95] and diplumblynes (62) [96] have all been isolated (Figure 5). Here, the lone pair effect on trans‐bent geometries is clearly observed as alkynes are linear whilst diplumbynes bear R−Pb−Pb angles of nearly 90°, and are therefore better described as diplumbylenes with a formal single bond and active lone pairs on each lead centre. [96]
Figure 5.
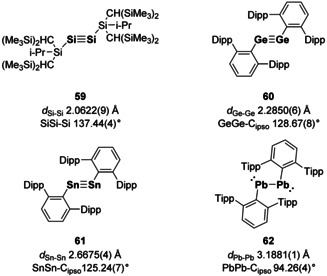
First reported examples of E14–E14 triple bonds. Dipp=2,6‐di‐iso‐propylphenyl. Tipp=2,4,6‐tri‐iso‐propylphenyl.
Homodiatomic E14 multiple bonds have been shown to react with a number of substrates including small molecules. [97] It was the latter that first drew the comparisons to transition metals,[ 14 , 15 ] as digermyne showed ambient temperature reactivity towards dihydrogen. [98] Even though disilenes are arguably the most studied E14 multiple bond, it was only recently that dihydrogen activation was achieved. [99] A highly trans‐bent and twisted disilene (63) was isolated, which is stabilised by sterically demanding N‐heterocyclic imine (NHI) ligands and hypersilyl (hypersilyl=Si(SiMe3)3) groups. Disilene 63 contains a long Si–Si double bond (2.3134(7) Å, average ≈2.22 Å), so can be best described as a weak double donor‐acceptor bond. On reaction with dihydrogen (1 bar) complete loss of the characteristic purple colour of 63 was observed within 10 minutes, this resulted in the formation of 1,2‐disilane (64, Scheme 14 a). [99] Notably, 64 is the result of anti‐addition, in contrast to alkene hydrogenation where syn‐addition is favoured. This experimental observation was explained through computational analysis as the staggered ligand arrangement reduces the stability, whilst pre‐organising the central Si=Si bond for concerted anti‐addition. [99] Disilene 63 has also been shown to react with other small molecules such as NH3, CO2 and O2. [100]
Scheme 14.
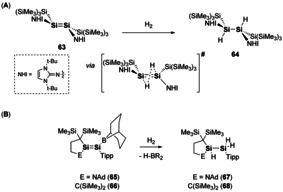
(a) Selective anti‐addition of dihydrogen to a highly trans‐bent and twisted disilene (b) Ligand controlled activation of dihydrogen.
Further examination of disilene dihydrogen activation was reported by Iwamoto.[ 101 , 102 ] This found that choice of stabilising ligand was key, as a π‐accepting boryl group was required in order to achieve cleavage of dihydrogen (65 and 66). When the boryl group was replaced with an alkyl substituent (iPr) no reactivity was observed. The rate of reaction could be further enhanced by use of a push‐pull disilene with a π‐donating amino substituent (65, Scheme 14 b).[ 101 , 102 ]
Other notable recent advances in disilene chemistry has focussed on the disilene‐silylsilylene equilibrium (R2Si=SiR2↔R3Si=SiR). This equilibrium has been previously inferred to explain unexpected reaction products and thermally induced rearrangements. For example, Inoue and co‐workers reported the formation of a tetrasilyldisilene (69) which was proven to exist as the disilene in solution but largely reacted as a silyl silylsilylene (69′, Scheme 15). [103] On leaving a solution of 69 at room temperature, C−H activation of the tBu group of bis(silyl)silylene (69′) is obtained to yield 70. [2+1]‐cycloaddition of ethylene occurs from 69′, rather than [2+2]‐cycloaddition of 69, to form 71. Dihydrogen activation was possible due to the ability to access 69′, whereas addition of NH3 occurs at the disilene (69) to yield the hydroaminated species 73 (Scheme 15). [103]
Scheme 15.
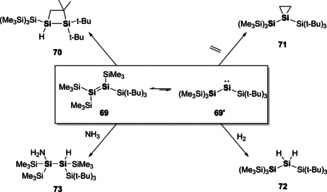
Reactivity at the disilene‐silylsilylene equilibrium.
Cowley and co‐workers found direct evidence for this disilene‐silylsilylene equilibria using a base‐coordination strategy. 4‐pyrollidinopyridine (4‐PPy) allowed for isolation of disilene 74. 4‐PPy was found to be labile and in the presence of excess NHC ligand, isomerisation to silylsilene 76 was achieved (Scheme 16). [104] This observation of 74 and 76 serves as direct evidence for the transient nature of 75 and 75′, which is also supported by computational studies. [104] The ability to control this equilibrium provides a new route to access to the more reactive silylsilylene species. Two‐coordinate acyclic silylenes are highly reactive species as they contain a vacant coordination site and a lone pair, and as such have shown facile bond activations towards small molecules and a variety of substrates.[ 24 , 28 , 105 , 106 , 107 ] It could be envisaged that new catalytic cycles, based on the ability to control this equilibrium, could be achieved in a somewhat similar fashion to that depicted in Scheme 1 B. Wherein the multiple bond (disilene) is off cycle and the “active” species is the low valent main group centre (silylsilylene).
Scheme 16.
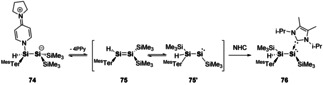
Intercepting the disilene‐silylsilylene equilibrium. MesTer=2,6‐bis(2,4,6‐trimethylphenyl)phenyl.
The first example of a main group multiple bond being employed in catalysis was reported by Sasamori and co‐workers. Digermyne 77 was found to be active in the catalytic trimerisation of a range of phenylacetylenes to yield regioselective 1,2,4‐triarylbenzenes (Scheme 17). [19] This reaction is specific to terminal arylacetylenes, as only stoichiometric reactions were observed with other unsaturated C−C bonds.[ 108 , 109 ] The key to enabling turnover with arylacetylenes is the proposed equilibrium that exists between compounds 79 and 80. Calculated energy barriers suggest that this is accessible at the higher temperatures (60 °C) at which the catalysis is performed. This equilibrium allows for access to the germole–germylene species (80) which contains the low valent GeII centre with a vacant coordination site for further substrate binding. The regioselectivity of this reaction is likely determined through the subsequent [1+2]‐cycloaddition and intramolecular [4+2]‐cycloaddition steps before release of the product and regeneration of digermene 78. It is proposed that digermyne 77 serves as a pre‐catalyst to this transformation with 78 as the resting state. [19]
Scheme 17.
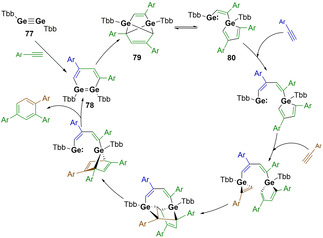
Digermyne catalysed cyclotrimerisation of alkynes. Tbb=4‐tBu‐2,6‐[CH‐(SiMe3)2]‐C6H2.
Advances in reactivity for the heaviest E14–E14 multiple bonds, that is, Sn and Pb, is somewhat hampered by their weak E14–E14 bonds and therefore tendency to dissociate in solution.[ 92 , 110 ] Recent studies by Power and co‐workers showed the reversibility of distannyne–stannylene in toluene solutions [111] as well as the reversibility of dihydrogen activation by distannynes. [112] Despite diplumbylenes being the first example of a heavier E14–E14 triple bond, it was only recently that further examples emerged. [113] A combined experimental and theoretical study found that London dispersion forces [31] were important in the stabilisation of diplumbylenes. Those which are less trans‐bent contain increased multiple bond character compared with their more trans‐bent counterparts (i.e. closer to 90°). [113]
E14−E14′ multiple bonds
Since Brook first reported the isolation of a silene, [3] several examples of metallaalkenes (R2E14=CR2, Figure 6) have been reported.[ 5 , 6 , 114 , 115 , 116 , 117 ] The reactivity of these metallaalkenes have largely focussed on cycloaddition reactions of carbonyls and alkynes, where they have been found to follow the Woodward–Hoffman selectivity rules. [118] Other E14=C containing species are metallavinylidenes (:E14=CR2, Figure 6) where the terminal E14 contains both an empty p‐orbital and a lone pair. In general, these compounds are reactive intermediates and require Lewis base stabilisation, however they have been shown to be ambiphillic in nature. [119]
Figure 6.

Different types of E14=C double bonds.
Extension towards E14‐C triple bonds have also been achieved, both Ge [120] and Sn [121] derivatives were evidenced as transient species upon photolysis of their corresponding diazomethanes. Using a similar strategy, Kato and Baceiredo were able to isolate a base‐stabilised silyne (82, Scheme 18). [122] This compound is stable up to −30 °C, however, above this temperature it undergoes a 1,2‐migration of the supporting ligand to form a phosphaalkene (83, Scheme 18). Furthermore, the carbenic character of 82 was shown via trapping with tert‐butyl isocyanide to form a keteneimine (84, Scheme 18). [122]
Scheme 18.
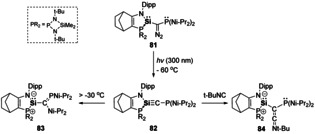
Synthesis and reactivity of a silyne (Si‐C triple bond).
The heavier mixed alkenes (i.e. E14=E14′, where E=Si, Ge, Sn) are proposed to have similar π‐bond strengths to their corresponding homo‐diatomic multiple bonds (e.g. Ge=Ge and Ge=Si are similar). [123] Whilst the synthesis and reactivity of metallaalkenes (E14=C) is rather well established, the heavier analogues are rare in comparison.[ 6 , 114 ] An example of a silastannene (85) was found to react according to the polarity of the double bond with phenols and thiophenols (Scheme 19 a). [124] Whilst the reaction of dioxygen with germastannene (88) results in coordination and formation of a 4‐membered ring (89, Scheme 19 b). [125]
Scheme 19.
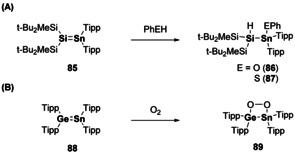
(a) Reactivity of silastannenes and (b) reactivity of germastannenes. Tipp=2,4,6‐tri‐iso‐propylphenyl.
Other examples of mixed E14 multiple bonds are found within small inorganic ring systems [126] and even as heteroallenes (R2E14=E14=E14R2).[ 127 , 128 ] Although the latter complexes may be better described as containing a zerovalent central atom which is supported by coordinated tetrylenes (i.e. R2E14→E14←E14R2).[ 32 , 129 ]
E14–E15 multiple bonds
It was not until 1981 that Becker reported the first example of a heavier E14−E15 bond (C≡P, phosphaalkyne). [4] Since this report, many examples of phosphaalkenes have emerged and, as such, are beyond the scope of this article.[ 130 , 131 ] Additionally, a range of silaimines have been isolated, which show increased reactivity compared to their imine counterparts. Their reactivity is also well documented and therefore will not be discussed herein.[ 132 , 133 , 134 , 135 , 136 ] Heavier imine analogues (Ge, Sn)[ 6 , 137 , 138 ] have also been isolated although are much rarer in contrast to silaimines. A recent study by Fulton and co‐workers showed that reactivity of a germanimine (90) exhibits “metalloid” type behaviour. The reactivity of 90 resembles that of transition metal imido complexes on reaction with heterocumulenes ([2+2]‐cycloaddition to form compounds 91 and 92, Scheme 20 a), and that of imines as Diels–Alder reactivity was also observed ([4+2]‐cycloaddition, compounds 93–96, Scheme 20 b). [139]
Scheme 20.
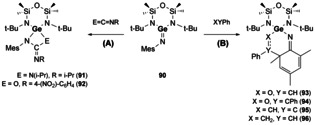
Metalloid behaviour of a germanimine (90).
Heavier combinations of E14−E15 are also known, of which silaphosphines are the most common and have recently been reviewed. [140] Examples of Ge and Sn‐phosphorous complexes are rare, but a recent example by Inoue and co‐workers showed that heavier nitrile analogues have interesting properties. [141] Use of N‐heterocyclic phosphinidene (NHCPs) ligands allowed for the isolation of compounds 97 and 98 (Scheme 21). These compounds contain short E14−P bonds and were additionally shown through DFT calculations to contain some multiple bond character, due to the resulting resonance structures. Surprisingly, compounds 97 and 98 showed no reactivity towards small molecules (H2, CO and CO2), however interesting reversible reactivity towards diphenylketene was observed (Scheme 21). [2+2]‐cycloaddition occurs at room temperature, however, on heating 99 (80 °C) and 100 (100 °C) retro‐cycloaddition of the ketene was achieved. [141]
Scheme 21.
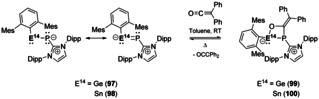
Heavier nitrile reversible reactivity with diphenylketene.
This reversibility prompted the examination of 97 and 98 in catalysis. Both compounds were found to be catalytically active in the hydroboration of aldehydes and ketones, with low loadings and fast reaction times at room temperature observed. [141] This preliminary study highlights the potential for these heavier multiple bonds in catalysis. Particularly those of Ge and Sn wherein the stability of the lower oxidation state increases compared to the lighter congeners. Other recent achievements within E14−E15 multiple bonds have resulted in the first examples of a stibasilene [142] (Si–Sb double bond) and an arsagermene [143] (Ge‐As double bond). Albeit, no reactivity has been reported.
E14–E16 multiple bonds
E14–E16 multiple bonds are probably the most widely studied, if you consider carbonyl containing compounds and efforts in the use of CO2 as a C1 feedstock for commodity chemicals. [144] In contrast heavier carbonyls are rare due to the high polarity of the resulting E14−E16 bond. This, however, does have its advantages as poly(siloxanes) (R2SiO)n have found widespread material use. It was not until the last decades that Kipping's dream [145] was realised and now several examples of silanones (i.e. compounds containing a Si=O double bond) have been isolated. [146] The high reactivity and instability of Si=O bonds was shown by Inoue and co‐workers, in which the first acyclic three‐coordinate silanones (101 and 102) were found to react with small molecules such as CO2 and methanol. [147] The acyclic silanones (101 and 102) are indefinitely stable in the solid state but in solution they decompose readily (t1/2 for 101 is 7 h in C6D6). Interestingly, monitoring solutions of 101 and 102 revealed different migration pathways depending on the different substitution at the supporting silyl ligand (Scheme 22). In the case of SiMe3 substituents (101) a 1,3‐silyl migration was observed to form an intermediate disilene complex (103), analogous to keto‐enol isomerisation. However, use of a super silyl supporting ligand (tBu3Si, Compound 102) results in formation of a two‐coordinate N,O‐silylene (104). The differing reactivity of the two complexes was shown on reaction with ethylene (Scheme 22). The intermediate disilene (103) undergoes [2+2]‐cycloaddition to form a four‐membered ring (105) whereas the silylene (104) forms a three‐membered ring (106). [147]
Scheme 22.
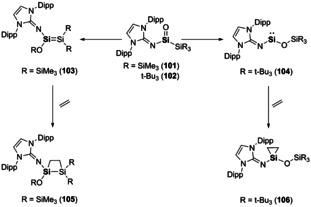
Ligand dependant transformations of silanones and subsequent reactivity with ethylene.
Further reactivity of 102 has shown the potential of multiple bonds in synthesis. One of the versatile reactions in the organic chemist's toolkit is the Wittig reaction, wherein carbonyl compounds are used to prepare alkenes. As such, it was shown by Inoue and co‐workers that analogous reactivity is in fact possible with heavier carbonyls. [148] This sila‐Wittig reactivity is shown to be possible with a range of non‐stabilised ylides (Scheme 23) resulting in high selectivity towards the Z‐silenes. This reactivity shows the similarities that can be found between carbon and silicon. Additionally, this provides new synthetic routes to silaalkenes.
Scheme 23.
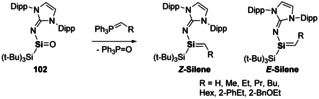
Sila‐Wittig reactivity of silanones, a new synthetic route to silenes.
Whilst silanones are somewhat established, examples of silaldehydes remain rare due to their reduced kinetic stabilisation. Lewis acid and base stabilisation methods enabled isolation of silaaldehydes, but single bond character was observed due to the push‐pull stabilisation.[ 149 , 150 , 151 , 152 , 153 ] Reports of the reactivity of such compounds are also scarce. However, the Lewis acid‐base stabilised silaaldehyde (107) revealed its carbonyl like reactivity (Scheme 24), on its reaction with phosphine which afforded the thermally stable silaphosphene (108). [153]
Scheme 24.
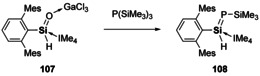
Silaphosphene synthesis from silaaldehydes. IMe4=1,3,4,5‐tetramethyl‐imidazol‐2‐ylidene.
Heavier E14–O multiple bonds, that is, Ge, Sn, and Pb, are known but are much rarer in comparison to the silicon analogues. [146] The first example of a monomeric germanone was reported by Tamao and co‐workers. It was found to undergo a series of addition reactions highlighting the high nucleophilicity of the oxygen atom in comparison to ketones. [154] Silanone analogues with heavier chalcogens, Si=E16 (E16=S, Se, Te) have been isolated, including the aldehyde analogues.[ 155 , 156 , 157 , 158 ] The NHC‐stabilised cationic silyliumylidene 109 enabled access to a series of Si=E16 complexes.[ 158 , 159 , 160 ] The reaction of 109 with elemental S, Se or Te afforded the desired chalcogen complexes (compounds 110–112, Scheme 25), with Si now in the +4 oxidation state. [160] Interestingly, compound 109, with Si in the +2 oxidation state, could be reformed on reaction with AuI, due to chalcogen transfer to the soft coinage metal. Additionally, chalcogen exchange reactions highlight preference for Si=S bond formation as the reaction of 111 and 112 with elemental sulphur results in the formation of compound 110. No reactivity of 110 was observed with Se or Te. [160]
Scheme 25.
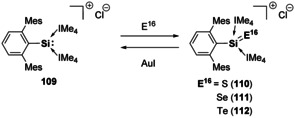
SiII/SiIV formation via silicon chalcogen multiple bond formation and chalcogen abstraction.
Descending group 14, examples of Ge−S, Se and Te multiple bonds exist.[ 161 , 162 , 163 ] Germanethiones and germaneselones were found to undergo a series of cycloadditions with unsaturated substrates, for example [2+2]‐cycloaddition with phenylisothiocyanate and [3+2]‐cycloaddition with mesitonitrile oxide. [163]
Conclusions and Outlook
Main group multiple bonds have proven themselves to be a powerful tool in the modern main group chemist's toolkit. Whilst a large variety and combinations of E13/E16 multiple bonds now exist, the reactivity of these complexes has only really begun to emerge in the last decades. This has particularly been exemplified by the discovery that main group multiple bonds contain transition metal like properties and are therefore capable of facile activation of strong bonds such as dihydrogen. One of the key factors for the development of this chemistry has been the correct choice of supporting ligands. Not only has this enabled the isolation of the multiple bond, but also has a direct influence on the reactivity. For example, comparison of the recently isolated dialumenes (Al=Al double bond) moving from a silyl‐based ligand to an aryl ligand now enables dihydrogen activation. This is also observed with Braunschweig's diborynes (B≡B triple bond) with the difference in the ligands controlling the reactivity towards CO and H2.
Main group multiple bonds have also shown more than just small molecule reactivity. Their use in synthesis has also been highlighted enabling new routes to functionalised compounds. For example, the use of a boron‐oxygen double bond as an O‐transfer reagent, as well as silicon‐oxygen bonds in sila‐Wittig reactivity, the latter of which has enabled isolation of new silaethenes which also display novel reactivity.
Finally, examples of multiple bonds in catalysis have begun to emerge. Digermynes and dialumenes have shown the stability of these dinuclear systems is key to enabling turnover. It is anticipated that many more examples of catalytic application of main group multiple bonds will emerge over the next decade. With parallels being drawn to transition metals, catalytic cycles such as those highlighted in Scheme 1 will become more obtainable as further understanding of the intrinsic nature of metal‐metal bonds is realised.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Biographical Information
Catherine Weetman obtained her MChem and Ph.D. at the University of Bath under the supervision of Prof. M. Hill in s‐block catalysis. Her first postdoctoral position was spent at the University of Edinburgh under Profs. P. Arnold and J. Love using d‐ and f‐block metals for bond activations and catalysis. Following this, she was awarded a postdoctoral fellowship to join Prof. S. Inoue at TU Munich, followed by a EuroTech Marie Curie Fellowship for Aluminium multiple bond chemistry which also included a six‐month research stay with Prof. M. Mazzanti at EPFL. In July 2020, Cath started her independent career at the University of Strathclyde as a Chancellor's Fellow.

Acknowledgements
Thank you to Dr. Martin Stanford and Dr. Amelie Porzelt for proof reading and useful insights. Thanks to the University of Strathclyde for the award of a Chancellor's Fellowship (C.W.).
C. Weetman, Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 1941.
References
- 1. West R., Fink M. J., Michl J., Science 1981, 214, 1343–1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Yoshifuji M., Shima I., Inamoto N., Hirotsu K., Higuchi T., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 4587–4589. [Google Scholar]
- 3. Brook A. G., Abdesaken F., Gutekunst B., Gutekunst G., Kallury R. K., J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1981, 191–192. [Google Scholar]
- 4. Becker G., Gresser G., Uhl W., Z. Naturforsch. B 1981, 36, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- 5. Power P. P., Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 3463–3504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Fischer R. C., Power P. P., Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3877–3923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Bag P., Porzelt A., Altmann P. J., Inoue S., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 14384–14387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Braunschweig H., Dewhurst R. D., Hammond K., Mies J., Radacki K., Vargas A., Science 2012, 336, 1420–1422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Kipping F. S., Sands J. E., J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1921, 119, 830–847. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Dohmeier C., Robl C., Tacke M., Schnockel H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1991, 30, 564–565; [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 1991, 103, 594–595. [Google Scholar]
- 11. Hofmann A., Tröster T., Kupfer T., Braunschweig H., Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 3421–3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Davidson P. J., Lappert M. F., J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1973, 317a. [Google Scholar]
- 13. Goldberg D. E., Harris D. H., Lappert M. F., Thomas K. M., J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1976, 261–262. [Google Scholar]
- 14. Power P. P., Nature 2010, 463, 171–177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Weetman C., Inoue S., ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 4213–4228. [Google Scholar]
- 16. Hill M. S., Liptrot D. J., Weetman C., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 972–988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Powers I. G., Uyeda C., ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 936–958. [Google Scholar]
- 18. Liddle S. T., Mills D. P., Dalton Trans. 2009, 5592–5605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Sugahara T., Guo J. D., Sasamori T., Nagase S., Tokitoh N., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3499–3503; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 3557–3561. [Google Scholar]
- 20. Weetman C., Bag P., Silvási T., Jandl C., Inoue S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10961–10968; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 11077–11081. [Google Scholar]
- 21. Hicks J., Vasko P., Goicoechea J. M., Aldridge S., Nature 2018, 557, 92–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Hicks J., Vasko P., Goicoechea J. M., Aldridge S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 10.1002/anie.202007530; [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2020, 10.1002/ange.202007530. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Hobson K., Carmalt C. J., Bakewell C., Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 6942–6956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Fujimori S., Inoue S., Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 3131–3142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Kong R. Y., Crimmin M. R., Dalton Trans. 2020, 10.1039/D0DT01564D. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Melen R. L., Science 2019, 363, 479–484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Zhong M., Sinhababu S., Roesky H. W., Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 1351–1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Yadav S., Saha S., Sen S. S., ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 486–501. [Google Scholar]
- 29. Rivard E., Power P. P., Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 10047–10064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Moilanen J., Power P. P., Tuononen H. M., Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 10992–11000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Liptrot D. J., Power P. P., Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0004. [Google Scholar]
- 32. Frenking G., Tonner R., Klein S., Takagi N., Shimizu T., Krapp A., Pandey K. K., Parameswaran P., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5106–5139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Zhao L., Hermann M., Holzmann N., Frenking G., Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 344, 163–204. [Google Scholar]
- 34. Nesterov V., Reiter D., Bag P., Frisch P., Holzner R., Porzelt A., Inoue S., Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9678–9842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Wang Y., Quillian B., Wei P., Wannere C. S., Xie Y., King R. B., Schaefer H. F., Schleyer P. V. R., Robinson G. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12412–12413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Hardman N. J., Wright R. L., Phillips A. D., Power P. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2842–2844; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2002, 114, 2966–2968. [Google Scholar]
- 37. Wright R. J., Phillips A. D., Hardman N. J., Power P. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 8538–8539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Wright R. J., Phillips A. D., Hino S., Power P. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 4794–4799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Arrowsmith M., Braunschweig H., Stennett T. E., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 96–115; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 100–120. [Google Scholar]
- 40. Bag P., Weetman C., Inoue S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 14394–14413; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 14594–14613. [Google Scholar]
- 41. Braunschweig H., Dellermann T., Dewhurst R. D., Ewing W. C., Hammond K., Jimenez-Halla J. O. C., Kramer T., Krummenacher I., Mies J., Phukan A. K., Vargas A., Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 1025–1028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Böhnke J., Braunschweig H., Dellermann T., Ewing W. C., Hammond K., Jimenez-Halla J. O. C., Kramer T., Mies J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 13801–13805; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 14006–14010. [Google Scholar]
- 43. Arrowsmith M., Böhnke J., Braunschweig H., Celik M. A., Dellermann T., Hammond K., Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 17169–17172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Stoy A., Böhnke J., Jiménez-Halla J. O. C., Dewhurst R. D., Thiess T., Braunschweig H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5947–5951; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 6055–6059. [Google Scholar]
- 45. Weetman C., Porzelt A., Bag P., Hanusch F., Inoue S., Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 4817–4827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Zhu Z., Wang X., Peng Y., Lei H., Fettinger J. C., Rivard E., Power P. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 2031–2034; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 2065–2068. [Google Scholar]
- 47. Caputo C. A., Guo J.-D., Nagase S., Fettinger J. C., Power P. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7155–7164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Caputo C. A., Koivistoinen J., Moilanen J., Boynton J. N., Tuononen H. M., Power P. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1952–1960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Caputo C. A., Power P. P., Organometallics 2013, 32, 2278–2286. [Google Scholar]
- 50. Wright R. J., Brynda M., Power P. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5953–5956; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 6099–6102. [Google Scholar]
- 51. Su J., Li X.-W., Crittendon R. C., Robinson G. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 5471–5472. [Google Scholar]
- 52. Hofmann A., Légaré M.-A., Wüst L., Braunschweig H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 9776–9781; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 9878–9883. [Google Scholar]
- 53. Braunschweig H., Krummenacher I., Légaré M.-A., Matler A., Radacki K., Ye Q., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1802–1805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Légaré M.-A., Bélanger-Chabot G., Dewhurst R. D., Welz E., Krummenacher I., Engels B., Braunschweig H., Science 2018, 359, 896–900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Zhao J., Xu B., Yu W., Wang X., Organometallics 2016, 35, 3272–3280. [Google Scholar]
- 56. Nakata N., Sekiguchi A., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 422–423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Franz D., Szilvási T., Pöthig A., Inoue S., Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 11036–11041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Nakata N., Sekiguchi A., Chem. Lett. 2007, 36, 662–663. [Google Scholar]
- 59. Leitao E. M., Jurca T., Manners I., Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Malik M. A., Afzaal M., O'Brien P., Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4417–4446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Li J. F., Li X. F., Huang W., Hu H. F., Zhang J. Y., Cui C. M., Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 15263–15266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Anker M. D., Schwamm R. J., Coles M. P., Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2288–2291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Heilmann A., Hicks J., Vasko P., Goicoechea J. M., Aldridge S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4897–4901; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 4927–4931. [Google Scholar]
- 64. Wright R. J., Brynda M., Fettinger J. C., Betzer A. R., Power P. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12498–12509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Hardman N. J., Cui C., Roesky H. W., Fink W. H., Power P. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2172–2174; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2001, 113, 2230–2232. [Google Scholar]
- 66. Wright R. J., Phillips A. D., Allen T. L., Fink W. H., Power P. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 1694–1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Anker M. D., Lein M., Coles M. P., Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 1212–1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Rivard E., Merrill W. A., Fettinger J. C., Power P. P., Chem. Commun. 2006, 3800–3802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Rivard E., Merrill W. A., Fettinger J. C., Wolf R., Spikes G. H., Power P. P., Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 2971–2978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Linti G., Nöth H., Polborn K., Paine R. T., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1990, 29, 682–684; [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 1990, 102, 715–717. [Google Scholar]
- 71. Price A. N., Cowley M. J., Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 6248–6252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Price A. N., Nichol G. S., Cowley M. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9953–9957; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 10085–10089. [Google Scholar]
- 73. Graham C. M. E., Millet C. R. P., Price A. N., Valjus J., Cowley M. J., Tuononen H. M., Ragogna P. J., Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 672–680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Davis J. R., Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys, ASM International, Almere, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 75. Franz D., Inoue S., Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 9385–9397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Braunschweig H., Radacki K., Schneider A., Science 2010, 328, 345–347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Loh Y. K., Porteous K., Fuentes M. Á., Do D. C. H., Hicks J., Aldridge S., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8073–8077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Dielmann F., Back O., Henry-Ellinger M., Jerabek P., Frenking G., Bertrand G., Science 2012, 337, 1526–1528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Anker M. D., Coles M. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 18261–18265; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 18429–18433. [Google Scholar]
- 80. Hicks J., Heilmann A., Vasko P., Goicoechea J., Aldridge S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17265–17268; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 17425–17428. [Google Scholar]
- 81. Anker M. D., McMullin C. L., Rajabi N. A., Coles M. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 12806–12810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Anker M. D., Coles M. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 13452—134550; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 13586–13589. [Google Scholar]
- 83. Franz D., Szilvasi T., Irran E., Inoue S., Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10037–10042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Kuchta M. C., Parkin G., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 12651–12652. [Google Scholar]
- 85. Kuchta M. C., Bonanno J. B., Parkin G., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 10914–10915. [Google Scholar]
- 86. Kuchta M. C., Parkin G., Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 2492–2493. [Google Scholar]
- 87. Kuchta M. C., Parkin G., J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1998, 2279–2280. [Google Scholar]
- 88. Clayden J., Greeves N., Warren S., Organic Chemistry , 2nd ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 89. Präsang C., Scheschkewitz D., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 900–921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Rammo A., Scheschkewitz D., Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 6866–6885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Kira M., Iwamoto T. in Advances in Organometallic Chemistry, Vol. 54 (Eds.: West R., Hill A. F.), Academic Press, 2006, pp. 73–148. [Google Scholar]
- 92. Power P. P., J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1998, 2939–2951. [Google Scholar]
- 93. Sekiguchi A., Kinjo R., Ichinohe M., Science 2004, 305, 1755–1757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Stender M., Phillips A. D., Wright R. J., Power P. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1785–1787; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2002, 114, 1863–1865. [Google Scholar]
- 95. Phillips A. D., Wright R. J., Olmstead M. M., Power P. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 5930–5931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Pu L., Twamley B., Power P. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 3524–3525. [Google Scholar]
- 97. Guo J.-D., Sasamori T., Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 3800–3817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Spikes G. H., Fettinger J. C., Power P. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12232–12233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Wendel D., Szilvási T., Jandl C., Inoue S., Rieger B., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9156–9159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Wendel D., Szilvási T., Henschel D., Altmann P. J., Jandl C., Inoue S., Rieger B., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 14575–14579; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 14783–14787. [Google Scholar]
- 101. Kosai T., Iwamoto T., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18146–18149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Kosai T., Iwamoto T., Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 7774–7780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Reiter D., Holzner R., Porzelt A., Altmann P. J., Frisch P., Inoue S., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 13536–13546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Stanford M. W., Schweizer J. I., Menche M., Nichol G. S., Holthausen M. C., Cowley M. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1329–1333; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar]
- 105. Roesky H. W., J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 730, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- 106. Blom B., Gallego D., Driess M., Inorg. Chem. Front. 2014, 1, 134–148. [Google Scholar]
- 107. Muthukumaran N., Velappan K., Gour K., Prabusankar G., Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 377, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- 108. Sasamori T., Sugahara T., Agou T., Guo J.-D., Nagase S., Streubel R., Tokitoh N., Organometallics 2015, 34, 2106–2109. [Google Scholar]
- 109. Sugahara T., Guo J.-D., Sasamori T., Karatsu Y., Furukawa Y., Ferao A. E., Nagase S., Tokitoh N., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 89, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar]
- 110. Power P. P., Chem. Commun. 2003, 2091–2101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Lai T. Y., Tao L., Britt R. D., Power P. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 12527–12530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Wang S., Sherbow T. J., Berben L. A., Power P. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 590–593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Queen J. D., Bursch M., Seibert J., Maurer L. R., Ellis B. D., Fettinger J. C., Grimme S., Power P. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14370–14383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. Lee V. Y., Sekiguchi A., Organometallics 2004, 23, 2822–2834. [Google Scholar]
- 115. Sekiguchi A., Lee V. Y., Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 1429–1448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116. Ottosson H., Eklöf A. M., Coord. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 1287–1314. [Google Scholar]
- 117. Gusel′nikov L. E., Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003, 244, 149–240. [Google Scholar]
- 118. Milnes K. K., Pavelka L. C., Baines K. M., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1019–1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119. Leung W.-P., Chan Y.-C., So C.-W., Organometallics 2015, 34, 2067–2085. [Google Scholar]
- 120. Bibal C., Mazières S., Gornitzka H., Couret C., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 952–954; [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2001, 113, 978–980. [Google Scholar]
- 121. Setaka W., Hirai K., Tomioka H., Sakamoto K., Kira M., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2696–2697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122. Gau D., Kato T., Saffon-Merceron N., De Cózar A., Cossío F. P., Baceiredo A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6585–6588; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 6735–6738. [Google Scholar]
- 123. Windus T. L., Gordon M. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 9559–9568. [Google Scholar]
- 124. Sekiguchi A., Izumi R., Lee V. Y., Ichinohe M., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14822–14823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125. Schäfer A., Saak W., Weidenbruch M., Organometallics 2003, 22, 215–217. [Google Scholar]
- 126. He G., Shynkaruk O., Lui M. W., Rivard E., Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7815–7880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127. Iwamoto T., Masuda H., Kabuto C., Kira M., Organometallics 2005, 24, 197–199. [Google Scholar]
- 128. Escudié J., Ranaivonjatovo H., Organometallics 2007, 26, 1542–1559. [Google Scholar]
- 129. Frenking G., Hermann M., Andrada D. M., Holzmann N., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1129–1144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130. Le Floch P., Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 627–681. [Google Scholar]
- 131. Mathey F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 1578–1604; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2003, 115, 1616–1643. [Google Scholar]
- 132. Denk M., Hayashi R. K., West R., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 10813–10814. [Google Scholar]
- 133. Hesse M., Klingebiel U., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1986, 25, 649–650; [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 1986, 98, 638–639. [Google Scholar]
- 134. Kong L. B., Cui C. M., Organometallics 2010, 29, 5738–5740. [Google Scholar]
- 135. Samuel P. P., Azhakar R., Ghadwal R. S., Sen S. S., Roesky H. W., Granitzka M., Matussek J., Herbst-Irmer R., Stalke D., Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 11049–11054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136. Yuvaraj K., Jones C., Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 11961–11965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137. Barrau J., Escudie J., Satge J., Chem. Rev. 1990, 90, 283–319. [Google Scholar]
- 138. Rit A., Tirfoin R., Aldridge S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 378–382; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 386–390. [Google Scholar]
- 139. Evans M. J., Anker M. D., Mouchfiq A., Lein M., Fulton J. R., Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 2606–2609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140. Nesterov V., Breit N. C., Inoue S., Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 12014–12039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141. Nesterov V., Baierl R., Hanusch F., Ferao A. E., Inoue S., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14576–14580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142. Lee V. Y., Aoki S., Kawai M., Meguro T., Sekiguchi A., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6243–6246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143. Lee V. Y., Kawai M., Gapurenko O. A., Minkin V. I., Gornitzka H., Sekiguchi A., Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10947–10949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144. Allen S. D., Byrne C. M., Coates G. W. in Feedstocks for the Future, Vol. 921, American Chemical Society, 2006, pp. 116–129. [Google Scholar]
- 145. Kipping F. S., Lloyd L. L., J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1901, 79, 449–459. [Google Scholar]
- 146. Xiong Y., Yao S., Driess M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4302–4311; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 4398–4407. [Google Scholar]
- 147. Wendel D., Reiter D., Porzelt A., Altmann P. J., Inoue S., Rieger B., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17193–17198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148. Reiter D., Frisch P., Szilvási T., Inoue S., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 16991–16996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149. Yao S., Brym M., van Wüllen C., Driess M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4159–4162; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 4237–4240. [Google Scholar]
- 150. Ghadwal R. S., Azhakar R., Roesky H. W., Pröpper K., Dittrich B., Goedecke C., Frenking G., Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8186–8188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151. Fukuda T., Hashimoto H., Sakaki S., Tobita H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 188–192; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 196–200. [Google Scholar]
- 152. Do D. C. H., Protchenko A. V., Ángeles Fuentes M., Hicks J., Kolychev E. L., Vasko P., Aldridge S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 13907–13911; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 14103–14107. [Google Scholar]
- 153. Sarkar D., Nesterov V., Szilvási T., Altmann P. J., Inoue S., Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 1198–1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154. Li L., Fukawa T., Matsuo T., Hashizume D., Fueno H., Tanaka K., Tamao K., Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 361–365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155. Burchert A., Müller R., Yao S., Schattenberg C., Xiong Y., Kaupp M., Driess M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6298–6301; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 6395–6398. [Google Scholar]
- 156. Lutters D., Merk A., Schmidtmann M., Müller T., Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 9026–9032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157. Mück F. M., Kloß D., Baus J. A., Burschka C., Bertermann R., Poater J., Fonseca Guerra C., Bickelhaupt F. M., Tacke R., Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 14011–14021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158. Porzelt A., Schweizer I. J., Baierl R., Altmann J. P., Holthausen C. M., Inoue S., Inorganics 2018, 6, 54–68. [Google Scholar]
- 159. Ahmad S. U., Szilvási T., Irran E., Inoue S., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5828–5836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160. Sarkar D., Wendel D., Ahmad S. U., Szilvási T., Pöthig A., Inoue S., Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 16014–16018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161. Xiong Y., Yao S., Karni M., Kostenko A., Burchert A., Apeloig Y., Driess M., Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 5462–5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162. Tokitoh N., Matsumoto T., Manmaru K., Okazaki R., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 8855–8856. [Google Scholar]
- 163. Matsumoto T., Tokitoh N., Okazaki R., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 8811–8824. [Google Scholar]


