Fig. 2.
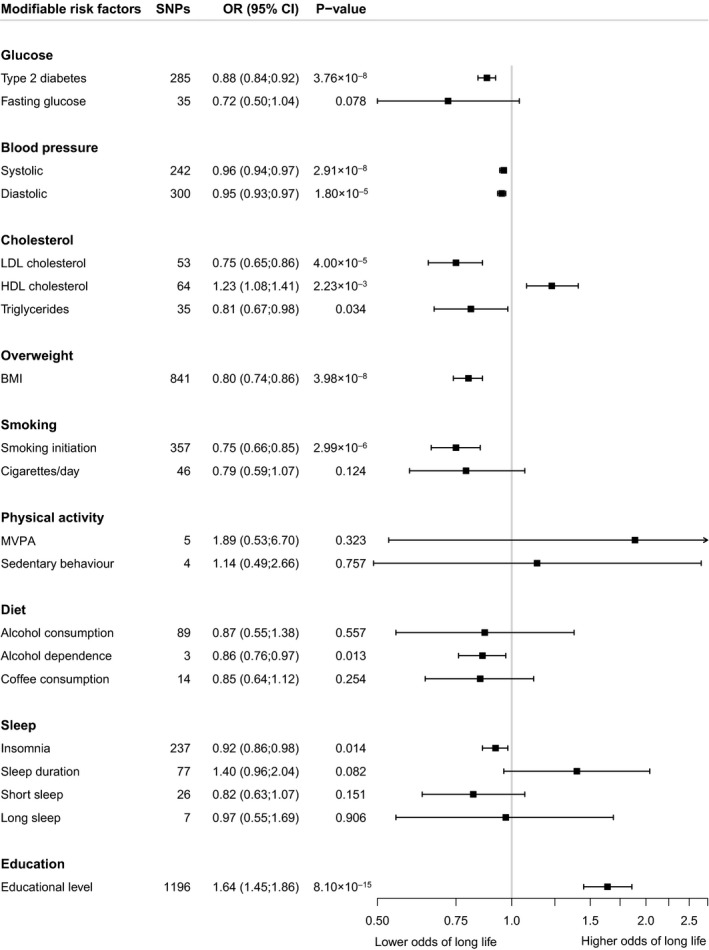
The association between modifiable risk factors and longevity beyond the 90thpercentile using the inverse variance‐weighted Mendelian randomization method. Odds ratios represent the associations with longevity of respectively: type 2 diabetes; 1‐mmol L‐1increase in fasting glucose; 1‐mmHg increase in SBP; 1‐mmHg increase in DBP; 1‐SD increase in LDL cholesterol; 1‐SD increase in HDL cholesterol; 1‐SD increase in triglycerides; 1‐SD increase in BMI; ever smoked regularly compared to never smoked; 1‐SD increase in number of cigarettes smoked per day; 1‐SD increase in log‐transformed alcoholic drinks/week; alcohol dependence; 50%‐change in coffee consumption; 1‐SD increase in MET‐minutes/week of MVPA; 1‐SD increase in sedentary time; insomnia; 1‐hour/day increase in sleep duration; <7 h sleep duration compared to 7–8 h; ≥9 h sleep duration compared to 7–8 h; 1‐SD increase in years of educational attainment. Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; HDL, high‐density lipoprotein; LDL, low‐density lipoprotein; MVPA, moderate‐to‐vigorous physical activity; OR, odds ratio.
