Figure 2.
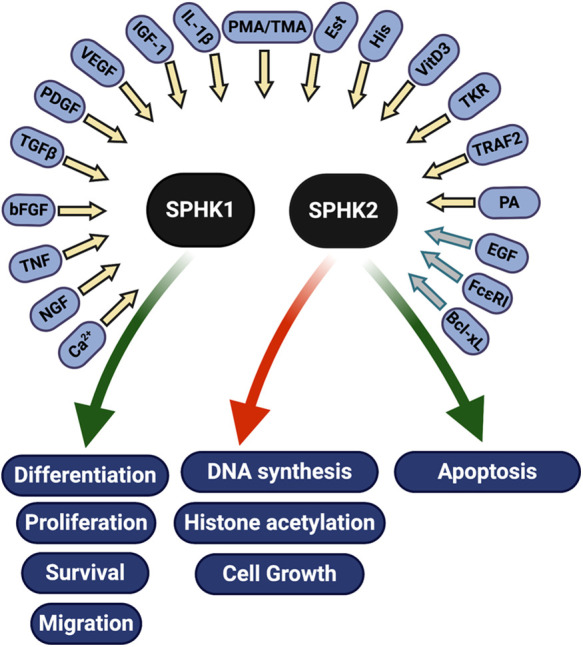
SPHKs are activated by a variety of factors, including cytokines, hormones, growth factors, small GTPases, tyrosine kinase receptors, FcεRI, and others. Following their activation, SPHKs promote (green arrows) or inhibit (red arrow) pathways that regulate cell health and death. Most factors activate SPHK1 (yellow arrows), whereas only a few are known to activate SPHK2 (gray arrows) (reviewed in 247–249). Bcl-xL,40 B cell lymphoma extra large; bFGF,236 fibroblast growth factor; Ca2+, calcium; EGF56,237; Est, estrogen237; FcεRI41, high-affinity IgE receptor; His, histamine238; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor; IL-1β239, interleukin 1 beta; NGF,240 nerve growth factor; PA, phosphatidic acid; PDGF241, platelet-derived growth factor; phorbol esters TMA238 and PMA242; TGF-β243, transforming growth factor beta; TKR,237 tyrosine kinase receptor; TNF244, tumor necrosis factor alpha; TRAF2,42 TNF-α receptor–associated factor 2; VEGF245, vascular endothelial growth factor; VitD3246, vitamin D3.
