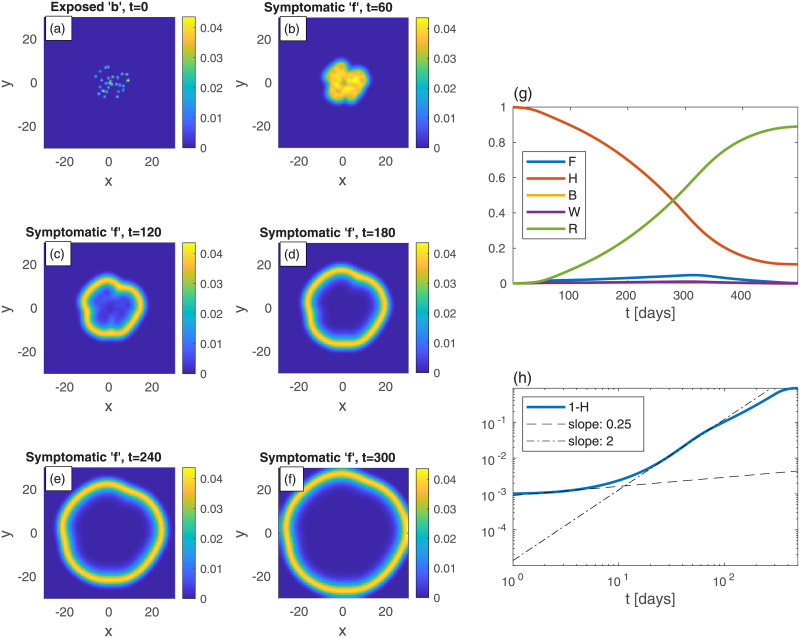
Fig 9.
(a)-(f): Time evolution of a epidemic starting from multiple random infection centers with uniform n, see (a); t is the time given in days, and x and y are the spatial Cartesian coordinates. The global value of b is the same as in previous figures, B = 10−3. All other populations are initially zero: w = f = r = 0. Both Dk and k are uniform. The symptomatic population f spreads and forms ring-like structures that expands in time. Panels (g) and (h) show (respectively) the different global populations and the cumulative infected population, 1 − H, vs time t.