Figure 7-11.
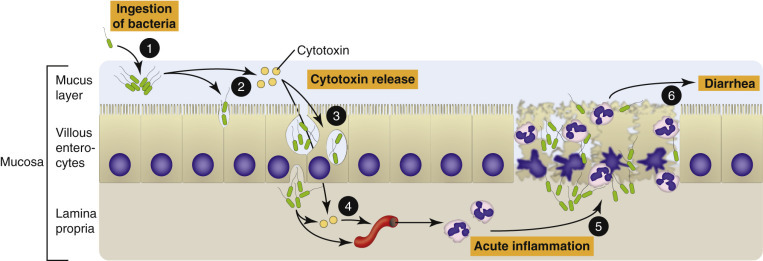
Mechanism of Invasive and Cytotoxin-Mediated Bacterial Inflammation.
1, Colonization of the mucosa. 2, Local production of cytotoxins and invasion of the mucosa by bacteria. 3, Bacteria replicate in large numbers and spread to adjacent epithelial cells. 4, Bacterial cytotoxins are released and injure adjacent mucosal endothelial cells and cause acute inflammation. 5, Acute inflammation results in necrosis of the mucosa. 6, Mucosal necrosis and bacterial toxins cause diarrhea.
(Courtesy Dr. H. Gelberg, College of Veterinary Medicine, Oregon State University; and Dr. J.F. Zachary, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Illinois.)
