Figure 2. Early prophylactic inhibition of RIP2 reduces eosinophilia and lung neutrophilia in an acute HDM model of asthma..
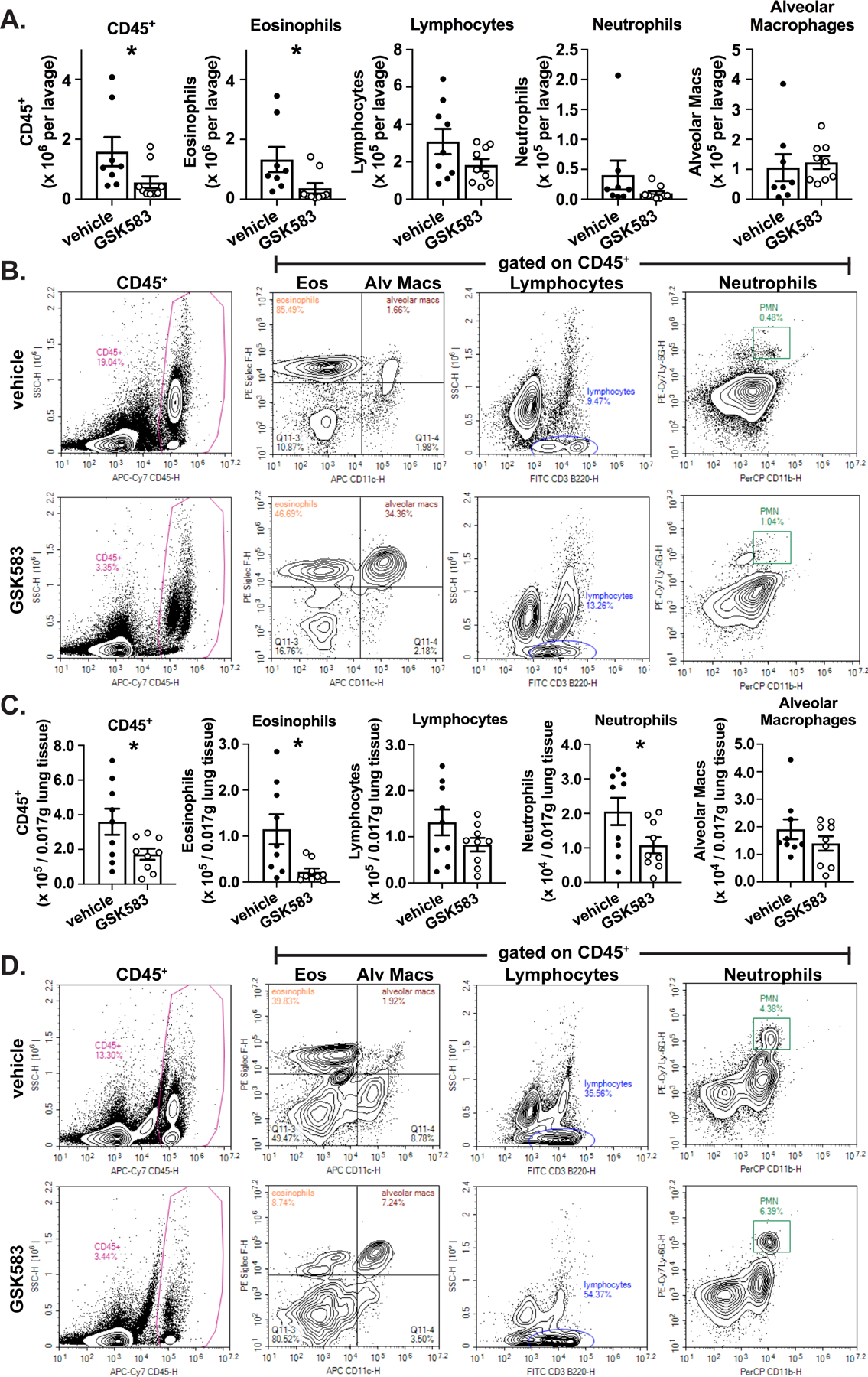
WT C57BL/6 mice were subjected to an acute HDM asthma model and were administered either regular chow or chow containing RIP2 inhibitor (GSK583) as indicated in Fig 1A. On day 14, mice were euthanized and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells or dissociated lung cells were isolated, stained for immune cell markers, and subjected to flow cytometric analysis. A). The total number of each cellular population within the BAL for vehicle compared to GSK583-treated mice. B.) Flow cytometry gating strategy for obtaining BAL cell counts in A.). C.) The numbers of each cellular population within a standardized amount of lung tissue is shown for vehicle compared to GSK583-treated mice. D.) Flow cytometry gating strategy for obtaining lung cell numbers in C.). Data are presented as scatterplots with bars where bar heights represent means ± SEM. Filled in circles represent individual datapoints for vehicle/control chow-treated mice and open circles represent individual datapoints for GSK583-treated mice. Data are pooled from 3 independent experiments for a total of n=8–9 mice per group (bloody lavage were excluded). Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test. *= p<0.05.
