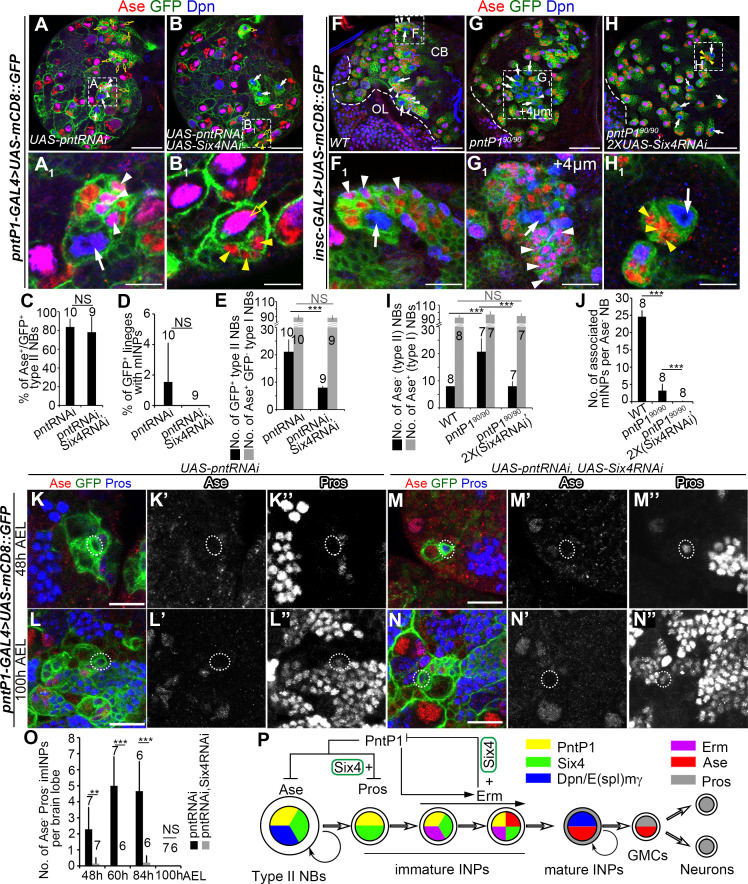
Fig 7. Six4 acts in newly generated imINPs to prevent premature differentiation of INPs.
Type II NB lineages are labeled by mCD8-GFP driven by pntP1-GAL4 (A-B1, K-N”) or insc-GAL4 (F-H1). Brains are counterstained with antibodies against Dpn, Ase and Pros. Scale bars equal 50μm in (A, B, F, G, H) or 10μm in (A1, B1, F1, G1, H1 and K-N”). (A-B1) An increased number of type II NBs is observed in PntP1 knockdown brain (A-A1) but not in a PntP1 and Six4 double knockdown brain (B-B1). However, ectopic Ase expression in type II NBs (open yellow arrows) is similarly observed in PntP1 knockdown (A-A1) and PntP1 and Six4 double knockdown (B-B1) brains. White arrows point to Ase- type II NBs. White arrowheads point to mINPs and yellow arrowheads to GMCs. (A1) and (B1) are enlarged views of the lineages highlighted with dashed squares in (A) and (B), respectively. (C-E) Quantifications of the percentage of Ase+ type II NBs (C), the percentage of type II NB lineages with mINPs (D), and total number of type II NBs or Ase+ GFP- type I NBs (E) in PntP1 knockdown or PntP1 and Six4 double knockdown brains. The number on top of each bar represents the number of brains examined. ***, p < 0.001; NS, not significant. (F-H1) The number of type II NBs is increased in pntP190 mutant brains (G) but remains the same in pntP190 mutant brains with the expression of UAS-Six4 RNAi driven by insc-GAL4 (H) as in the wild type (F). White arrows point to type II NBs and white arrowheads to mINPs. (F1, G1, and H1) are enlarged views of the areas highlighted with dashed squares in (F, G, and H), respectively, to show that mINPs are generated in the wild type (F1) and pntP190 mutant brains (G1) but not in the pntP190 mutant brains with the expression of UAS-Six4 RNAi (H1), which produce GMCs (yellow arrowheads) directly instead. (I-J) Quantifications of the number of Ase- type II NBs or Ase+ type I NBs/brain lobe (I) and number of mINPs per Ase- NB (J). The number on top of each bar represents the number of brains examined. ***, p < 0.001; NS, not significant. (K-L”) Ectopic nuclear Pros expression is not observed in the newly generated imINP (dotted circles) in a PntP1 knockdown type II NB lineage (K-K”) at 48hrs AEL but is detected in all newly generated imINPs at 100 hrs AEL (L-L”). (M-N”) Ectopic nuclear Pros is detected in all newly generated imINPs (dotted circles) in PntP1 and Six4 double knockdown type II NB lineage at 48 hrs (M-M”) and 100 hrs (N-N”) AEL. (O) Quantifications of the number of newly generated imINPs without the ectopic nuclear Pros expression in PntP1 knockdown and PntP1 and Six4 double knockdown brains. The number on top of each bar represents the number of brains examined. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; NS, not significant. (P) A schematic diagram shows potential functions of Six4 in type II NB lineage development. Late during imINP development, Six4 acts together with Erm to inhibit PntP1’s activity and expression, which ensures that imINPs become fate-committed mINPs instead of dedifferentiating into type II NBs. In the newly generated imINPs, Six4 also contributes to the inhibition of nuclear Pros expression, thus preventing premature differentiation of INPs into GMCs.